[This op-ed was originally published in the Cincinnati Business Courier on July 9, 2010. Visit the original op-ed for more comments, thoughts and opinions on how to effectively apply form-based codes – Randy.]
As Cincinnati officials move closer toward their goal of implementing some variation of form-based codes in Cincinnati it is important that the application is done correctly. Form-based codes, when done correctly, offer a simpler approach to land planning than their awkward land use/design overlay contemporary. In order to achieve the full benefits of a form-based code there are a few practices that should be followed.
Keep It Simple:
The problem with contemporary zoning codes is that they feature layers upon layers of regulations that are complicated to understand by the general public and developers. Most zoning codes have an underlying Euclidean Zoning Code which regulates land use and basic design elements like building setbacks, heights, and densities. Then in the more stringently regulated areas there are often overlay districts created that layer an additional set of regulations on top of the land use regulations. These overlay districts tend to focus more on design features within a given area, and allow any land use regulations that are not covered in their guidelines to fall back into the realm of the underlying zoning code.
The primary functional gain of form-based codes is that they presumably eliminate this layered zoning effect that creates confusion. As a result, form-based codes should NOT be implemented in a layering manner. Form-based codes should completely replace any existing overlay districts and all land use zoning codes that currently exist in the area. The end result would be a district that has only a code that regulates the urban form of an area without the constraints of land use controls and the arbitrary design standards set out therein.
The reason this is often not done is due to a fear that form-based codes will not have the teeth to prevent communities from being destroyed by “undesirable” uses. I assert that this fear is misguided as our current zoning practices were set out during an industrialization period in the United States that saw many polluting industries locating in or around residential neighborhoods. This is certainly not what is desired, but this will not occur in modern society for two main reasons.
- Industries locate based on transportation access. An industrial user will seek out access to freight rail, barge, air, and truck access, and as a result, this will eliminate the vast majority of our residential neighborhoods from consideration as they have self-selected to locate in areas away from these industrial amenities.
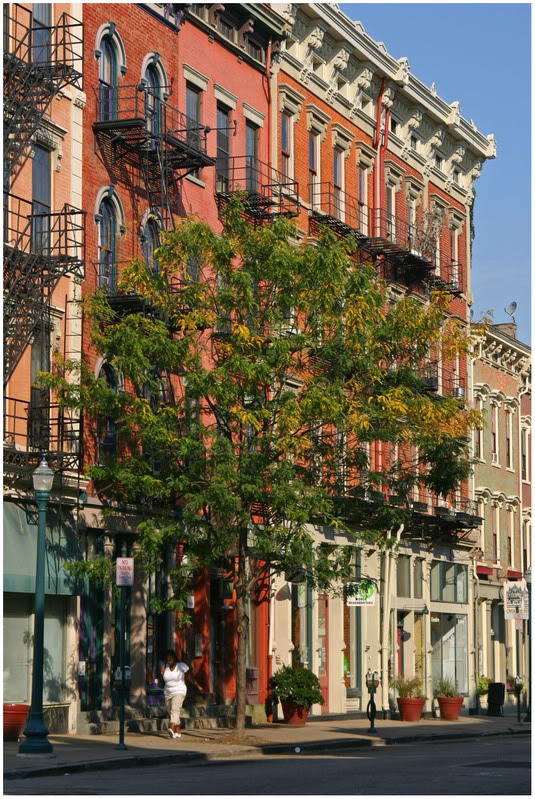
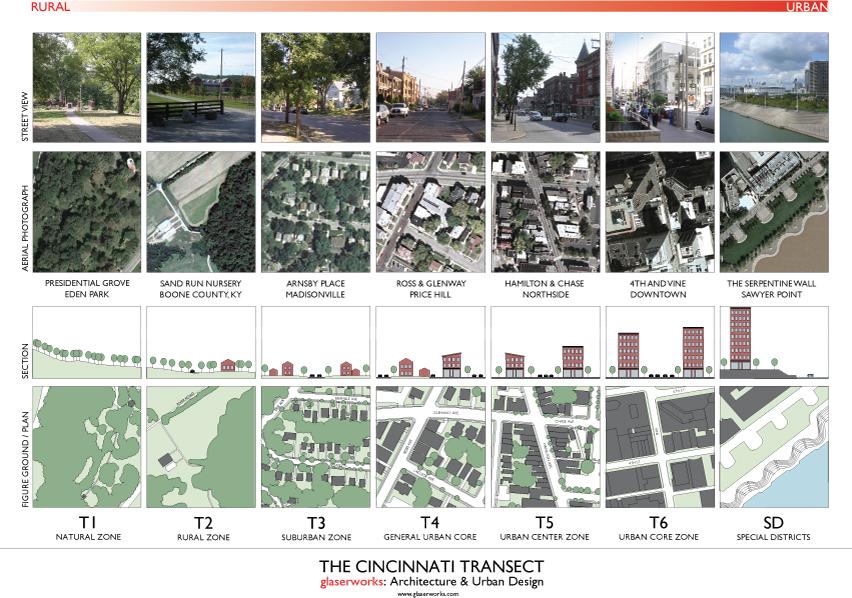
- If a form-based code is done well an “undesirable” will often not be able or willing to locate in a higher transect district. A good example would be Cincinnati’s T6 “Urban Core Zone” where presumably a coal cleaning facility could set up shop due to the lack of land use controls, but if it were to open, the coal cleaning facility would have to design its facility to fit the form of that found in the T6 Urban Core Zone. Such a form would not only be undesirable for such a use, but it would also be cost-prohibitive for its business function.
Forget the Piecemeal Approach:
Many form-based codes are applied in a piecemeal approach that selectively implements the form-based controls in a particular neighborhood or business district. In the Cincinnati region this is presently being done in both Bellevue, KY and Covington, KY as those cities incorporate form-based codes of their own.
The problem with this approach is that it ignores the all-important transect for which a form-based code is derived. The piecemeal approach allows for the individual form-based codes to be developed in an insular manner without taking into consideration the form of the urban region.
The reason this is problematic is that form-based codes are meant to be living, breathing creatures that can change as a community changes. Cincinnati’s center city has not always been as densely built as it is today, and it got to this point by growing and changing over time. This means that a code that can change with the city is more ideal than one that cannot. If a neighborhood or business district wants to evolve upward from T4 “General Urban Core” to a T5 “Urban Center Zone” it should be able to do so, but if that individual form-based code is developed without these other districts in mind, it prevents such evolution from taking place.
Form-based codes offer a variety of tangible benefits, but they can only fully be realized if we leave the fear of the unknown behind and truly take a risk on something bold and new. No major American city has embarked on such a dramatic reform of its land-planning techniques, but what better city is there than Cincinnati – where modern planning was first implemented – to explore such an effort?