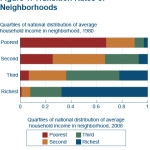
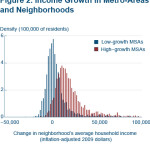
Data from the Cleveland Branch of the Federal Reserve Bank shows that a poor neighborhood’s income growth, while affected by internal factors, is also highly influenced by its surrounding metropolitan area.
Much the same that a poor family in a strong neighborhood is more likely to be lifted up by the rising tide in their neighborhood, it seems that poor areas of cities have the ability to function in the same manner.
The data from the Federal Reserve measures neighborhood growth, or lack thereof, from 1980 to 2008. Several statistics from the report come as a surprise.
First, while the report finds that a neighborhood’s percentage of residents with a high school degree, bachelor’s degree, and its unemployment rate in 1980 all have some correlation with that neighborhood’s chances of having income growth, the statistics are not all that strong.
The difference in bachelor’s degrees between neighborhoods with no income improvement and those with a high degree of income improvement was around 3%. Meanwhile, the unemployment rate was only about 2% lower in high income growth neighborhoods.
But perhaps the most striking evidence, at the local level, is how much population density correlates with a neighborhood’s likeliness to achieve high income growth.
Neighborhoods that had no improvement had, on average, a density of 12,028 people per square mile in 1980, while neighborhoods with high improvement had an average density more than double that of 30,399 people per square mile.
The City of Cincinnati, by comparison, has a population density around 3,810 people per square mile.
By 2008, the change is stark. Neighborhoods that received high income growth increased their educational attainment, population and population density at a much higher rate than what the report classifies as no-improvement neighborhoods.
The report also found that poor neighborhoods in low-growth metropolitan statistical areas (MSA) were more likely to remain stagnant or even shrink while poor neighborhoods in high-growth MSAs had a higher chance of experiencing income growth.
Growing at just 0.4% annually since the 2010 Census, the Cincinnati MSA would fall into that low-growth category.
While the average income of an MSA in 1980 may not be a good predictor of whether a neighborhood will experience high or low growth, neighborhoods that experienced high income growth were located in regions that experienced higher growth in income, a growing population and increased their population density.
As a result, two identical poor neighborhoods in New York City and Cleveland in 1980 would look much different in 2008, despite being in the same position 38 years prior. The assertion is that a growing metropolitan area has a tendency to lift the tide for all neighborhoods.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland points out, however, that some of this improvement in high-growth neighborhoods could be due to what they deem residential sorting; basically, changing demographics in the neighborhood.
While the evidence is not certain, the data also shows neighborhoods that experienced high-growth from 1980 to 2008 were also more likely to have gained residents (10%) than low-growth neighborhoods (-20.9%). Therefore, neighborhoods that experienced high growth were those that also had the greatest opportunity for demographic shifts to occur within the neighborhood.
Interestingly enough, while much of the gentrification argument has centered on white residents pushing out minorities, the report found that neighborhoods that experienced high growth rates were more likely to reduce their share of black and white residents, while increasing their share of Hispanic residents.
These trends have wide implications for American policy regarding poverty and urban development, but appear to be less relevant in the Cincinnati region where very few neighborhoods have any sizable Hispanic population.
With this strong evidence indicating population density is linked to a poor neighborhood’s ability to improve, it only reinforces the growing narrative about the suburbanization of poverty in America.
Still, however, there is a long way to go before this narrative is fully realized locally; as it is estimated that roughly half of all children in the City of Cincinnati live in poverty – a number that does not appear to be changing.
While policy makers at City Hall will surely be discussing youth jobs programs, career training, early childhood education and neighborhood health centers, one other item on the policy agenda should be the urban form of our region’s neighborhoods.
We do not know whether higher population densities were a cause or merely correlated with a neighborhood’s ability to improve, but we do know, thanks to this data from the Federal Reserve, that the two issues appear to be more connected than what we may have previously thought.