The brief tenure of Ohio Governor John Kasich (R) has been marked by repeated attacks on public transportation. Shortly after his inauguration, he returned a $400 million federal grant to begin passenger rail service between Cincinnati, Columbus and Cleveland. In April he corrupted ODOT’s Transit Review Advisory Committee, redirecting over $50 million allocated for the Cincinnati Streetcar to road projects in northern Ohio.
Lost amid these higher profile events was his rescinding of $150 million promised to the state’s transit agencies by former governor Ted Strickland (D). With its share, Queen City Metro planned to begin two new express services to Uptown. A direct service from West Chester fell victim to Kasich’s cuts, but with the help of a direct federal grant that Kasich could not block, Metro launched route 38X on December 5.
Each morning six buses now travel between Western Hills and all of Uptown’s major destinations including the University of Cincinnati, Good Samaritan Hospital, University Hospital, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, Veteran’s Hospital and Christ Hospital. The only major employment centers not directly served are the various Children’s hospital offices housed in the old Bethesda Hospital and Vernon Manor Hotel.

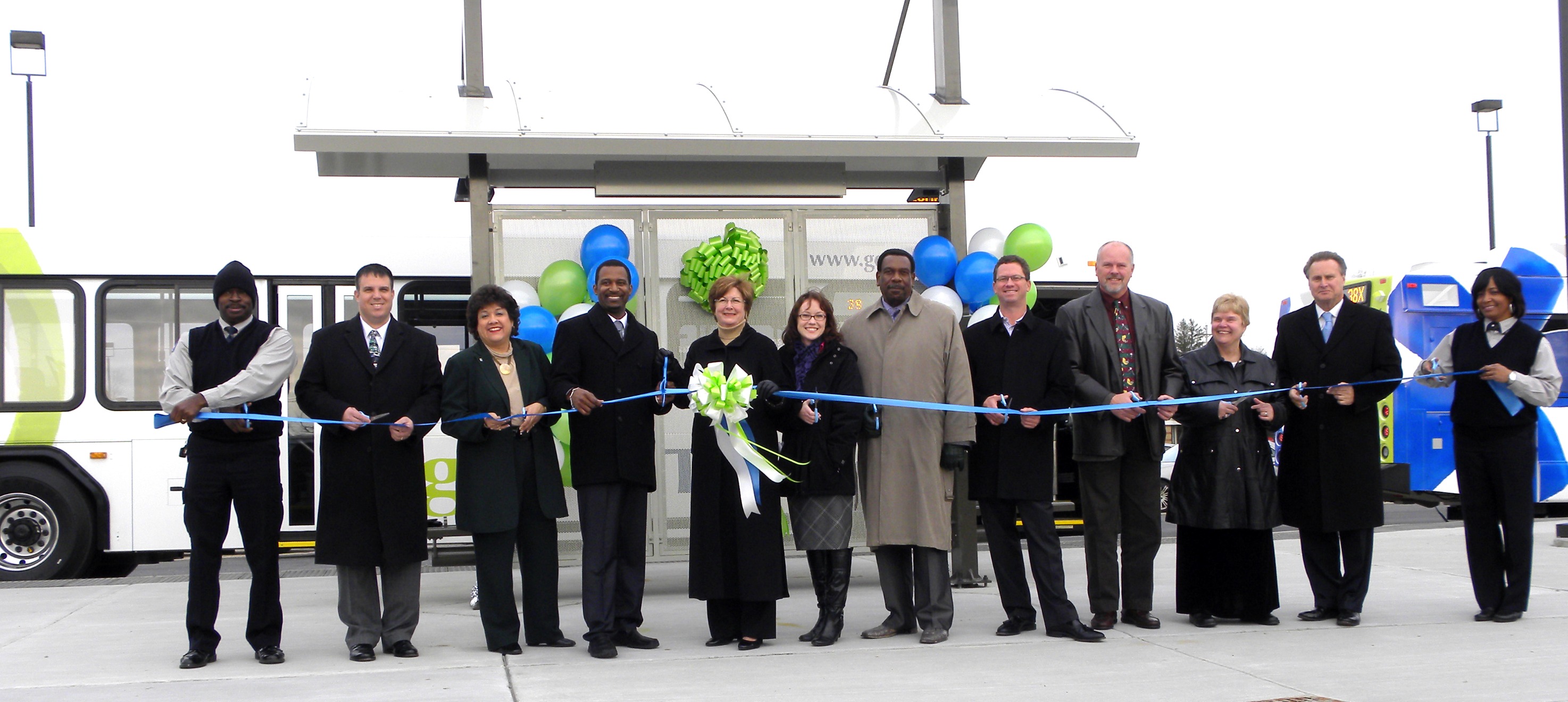
Cincinnati officials celebrate the opening of the new Glenway Crossing Transit Center on December 9, 2011.
The 38X buses begin and end each day at the Glenway Crossing Transit Center, a new bus transfer station in the Glenway Crossing Shopping Center that also serves the #39, #64 and #77X Delhi Express. It features shelters, several dozen park & ride parking spots for commuters, and restrooms for bus drivers.
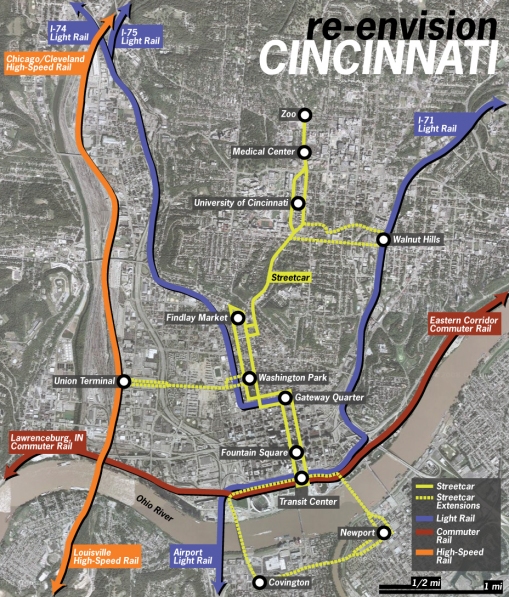
In concept the transit center resembles the dozen ‘transit hubs’ that were planned as part of the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority’s (SORTA) 2002 Metro Moves plan. Although that plan was best known for its five light rail lines, a half-cent sales tax would have also funded a dramatic expansion of bus service throughout Hamilton County.
Glenway Crossing was built in the late 1980s in place of the Chesapeake & Ohio’s (C&O) disused Cheviot Yard. In 1981, shortly before the railroad’s abandonment, the yard and the line it served were the subject of the Westside Transit Study, produced by the Ohio, Kentucky, Indiana Regional Council of Governments (OKI), which examined construction of a light rail line from downtown Cincinnati, via the unused subway beneath Central Parkway, to an ambitious transit oriented development (TOD) in Western Hills.
The line would have emerged from the old subway just north of Brighton, crossed I-75 and the Queensgate railroad yard on a new viaduct parallel to the Western Hills Viaduct, then climbed to Glenway Avenue on the C&O tracks. Midrise office buildings were to have been the focus of the Cheviot Yard TOD. The unused subway under Central Parkway was to have been extended south under Walnut Street or Vine Street to a station at Fountain Square.
SORTA planned to fund construction of this line, as well as a network of other light rail lines, with a countywide transit sales tax that failed at the polls in 1979 and 1980. Without funds available to purchase the C&O railroad when it was abandoned, SORTA was helpless to stop the railroad from being sold to dozens of different buyers. The expense necessary to purchase the right-of-way by power of eminent domain precluded this line from being part of SORTA’s failed 2002 Metro Moves network.