Analysis of data recently released by the Cincinnati Branch of the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland shows the area’s economy in a relatively healthy position compared to nearby metro areas, and to the nation as a whole.
LaVaughn Henry, Vice President and Senior Regional Officer at the Cincinnati Branch, says that he believes the region’s economy is poised for continued economic growth, and he points to several factors that contribute to his optimism – a highly educated workforce, an economy healthily spread amongst different sectors, and numerous Fortune 500 companies headquartered in the city.
When diving into the numbers, Henry points to 30% of the regional workforce holding a bachelor’s degree as an item that makes the city an attractive place to do business.
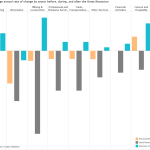
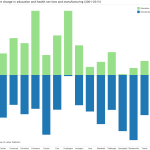
He also touts the city’s relatively low unemployment rate which stands at 5.2% – about even with Pittsburgh and a full percentage point better than the rates nationally and for the state of Ohio. Making the area’s economy even stronger is the fact that its top industry sectors – professional and business services, health and education, and skilled manufacturing – all continue to experience healthy growth.
The Federal Reserve also pointed to continued capital spending as a bright spot that is boosting employment and earnings. Specifically, two hospital expansions and the opening of General Electric’s Global Operations Center at The Banks are expected to support thousands of jobs through 2016.
While the data found that Cincinnati is out-performing many of its peers, it also found that it has room for improvement in terms of wage and GDP growth.
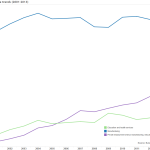
Wages, the Federal Reserve says, have yet to reach pre-recession levels locally, and, while growing, are growing modestly at best. Researchers say that Cincinnati is suffering from a national problem of too many workers in the labor market, and high growth in low-paying service sector jobs that depress wage data. And while the region’s gross domestic product is growing faster than the national average, economists note that, like wages, it has yet to reach pre-recession levels.
When compared to Pittsburgh and Cleveland, the only other two metropolitan regions with more than 2 million people in the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland district, Cincinnati is, by far, the healthiest performer.
In Cleveland economists note that its economy is recovering from the Great Recession much better than the recession of 2001, yet it continues to trail national averages. While unemployment is falling throughout the region, it remains stubbornly high at 6.8% – above both the national and state averages. A bright spot, however, is Cleveland’s 28.5% bachelor’s degree rate within the workforce is at least on-par with the national average.
Pittsburgh, meanwhile, recovered the quickest of the three from the Great Recession, but has since seen its economic indicators stall. While unemployment has consistently stayed below the national average, growth in almost all industries in the city was lower than the national average. And while GDP grew from 2009 to 2012, economists at the Federal Reserve expect the data to be somewhat more somber once data is released for 2013 and 2014.