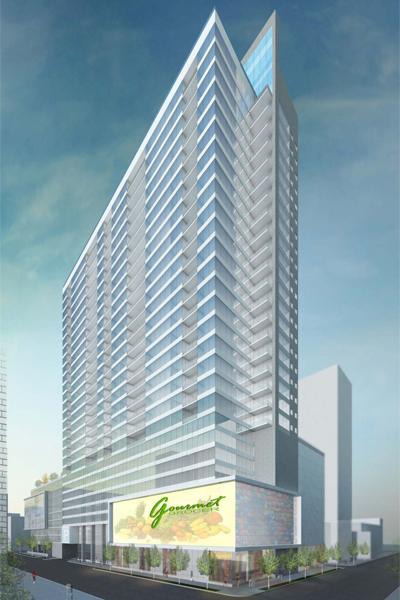
More than a year after an initial deal was proposed to redevelop the aging Pogue’s Garage site into a sleek residential tower, a new deal may actually move forward that will allow for construction to finally move forward.
In November 2013, the City of Cincinnati had entered into a Development Agreement with Flaherty & Collins to build a 15,000-square-foot grocery store, 950-space parking garage and a soaring 30-story residential tower with 300 units costing $94 million. As part of this deal, the City had committed to providing a $12 million forgivable loan to the project. This came after an initial deal to fund the project through the proceeds generated by the then proposed Parking Modernization & Lease program.
The Parking Modernization & Lease program, however, was almost immediately cancelled upon the arrival of Mayor John Cranley (D); who then subsequently stated that the $12 million forgivable loan for the project was “too rich”, and that the entire project should be rethought.
This led to the engagement of the Cincinnati Center City Development Corporation (3CDC), and the new deal that will go before City Council’s Neighborhoods Committee, chaired by Vice Mayor David Mann (D), at 2pm today.
According to a leaked memo from City Manager Harry Black’s office, the new deal is substantially different from the previous Development Agreement. Instead it calls for a $5.5 million grant to Flaherty & Collins to construct an eight-floor residential tower including 208 units, and a $4 million loan to 3CDC to construct a 925-space parking garage and 25,000 square feet of street-level retail space.
The Cranley Administration is touting the deal as a savings for taxpayers, while also not sacrificing too much.
“We inherited an overly rich deal,” Jay Kincaid, Mayor Cranley’s Chief of Staff, told UrbanCincy. “This new deal saves taxpayers $6.5 million, and gives the City control over the garage.”
Much of the savings is realized through the changes to the parking agreement. The previous deal provided the developer a grant to build and operate the parking structure, while the new deal utilizes a $4 million performing loan to be repaid later by 3CDC. Once the loan is paid off, the revenue stream from the parking structure would be shared by the three parties.
The emergency ordinance that will be put before the Neighborhoods Committee today, and then most likely be voted on by the full City Council on Wednesday, also includes a 30-year property tax abatement for the apartment component.
As of now, property tax abatements in Downtown and Over-the-Rhine filter 25% to Cincinnati Public Schools, with the remaining 75% being the actual realized abatement. Starting on January 1, 2015, however, that latter number would be reduced to 67.5% with the 7.5% difference being put into a fund to help cover the costs of operating and maintaining the Cincinnati Streetcar.
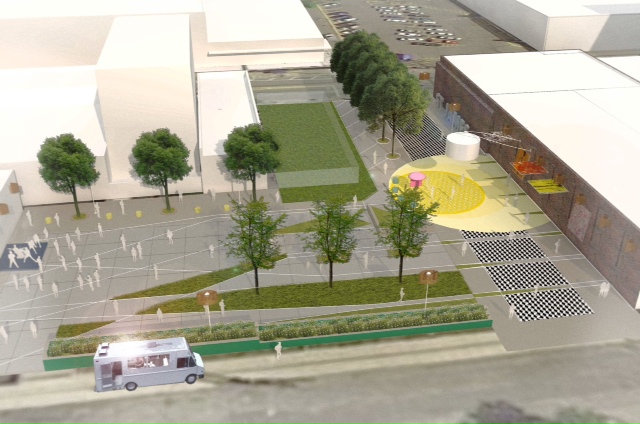
With the development losing approximately two-thirds of its height, but only one-third of its number of residential units, it signals that the new development will look quite different than the initial renderings released to the public. The final result may mean smaller residential unit sizes or a wider tower that utilizes more of the site’s footprint.
Yet unanswered is what will happen with Paragon Salon, which has remained in operation at the site despite being served eviction notices from the City. Since the original Development Agreement was signed more than a year ago, the owners of Paragon have claimed the City is violating their lease agreement, and has requested assistance in finding a new location. The City, meanwhile, has rebuffed Paragon and said they will not submit to paying for the costs of its relocation.
One item previously holding up construction on this still unnamed project was the redevelopment of Tower Place Mall into Mabley Place. Now that the parking garage is complete and open for business, City leaders say they feel more confident in closing down Pogue’s Garage to allow for construction to commence.







 Sanborn Fire insurance map from 1904. Courtesy of the Public Library of Cincinnati and Hamilton County
Sanborn Fire insurance map from 1904. Courtesy of the Public Library of Cincinnati and Hamilton County Modern day plan
Modern day plan