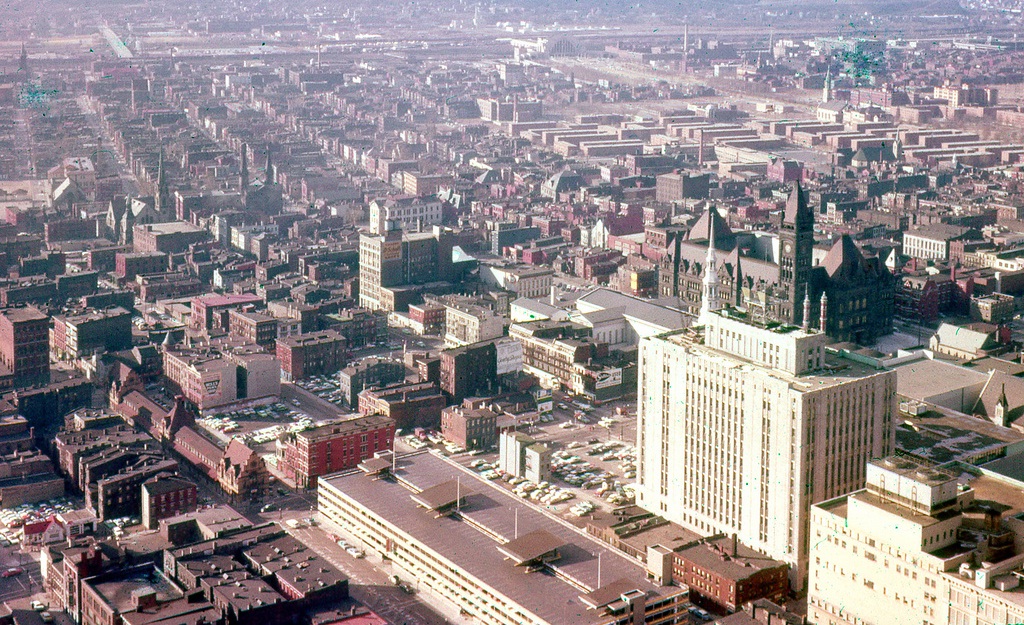
Cincinnati, like all peer cities, recorded its peak population in the 1950 and has steadily lost residents since. Specifically, Cincinnati has lost 205,000, or 43 percent of its peak population of 503,998 as recorded by the U.S. Census Bureau. Meanwhile, the population of Cincinnati’s metropolitan statistical area has doubled to 2.2 million.
Contrary to the narrative perpetuated by those who practice the politics of decline, this loss of population is symptomatic not of variously corrupt or negligent city officials but is rather the outcome of social trends that have evolved well outside the purview of city government. What’s more, nationwide demographic trends and elevated living standards mean attracting 205,000 new residents would require the City of Cincinnati to transform itself physically into something entirely unlike what it is at present or was in 1950.

Cincinnati’s population has taken a recent downward trajectory, but there may be more to the story. Chart produced by UrbanCincy.
Demographic Changes since 1950
Entirely overlooked in the public discussion of city population decline is the end of the postwar “Baby Boom” which was enabled by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration’s (FDA) approval of oral contraceptives in 1960, and the U.S. Supreme Court’s legalization of abortion in 1973. Between 1960 and 1975, the number of annual live births in the United States fell from 4.25 million to 3.1 million.
An academic assessment of how the plummeting birthrate affected Cincinnati’s population could consume weeks of research. But the drop in family size, along with the proliferation of separations and divorces, means nearly all Cincinnati homes and apartment units that were occupied by large families in the 1950s are today occupied by fewer people.
So for Cincinnati to regain its lost 205,000 residents, the number of people residing in existing homes and apartment units must increase dramatically, and new construction must be populated at something higher than today’s prevailing density. With no reason to expect that Cincinnati’s birthrate will suddenly increase to that of impoverished countries, all population growth must come from the city’s suburbs or from outside the region. The wealthier the newcomer, the more living space they can afford. So paradoxically, the successful pursuit of top talent frustrates the task of fitting 205,000 new residents within Cincinnati’s existing city limits.
Loss of Residential Neighborhoods
Cincinnati’s municipal boundaries have not changed since it achieved its peak population in 1950, but thousands of prewar homes and apartments have since been replaced by non-residential structures. This means Cincinnati not only lost tens of thousands of residents for construction of expressways, light industry, and other purposes, but these properties are generally unavailable today for any effort to repopulate the city.
Cincinnati’s loss of residents and residential land was not limited to expressway construction and urban renewal projects. In the neighborhoods collectively known as Uptown, physical growth of universities, hospitals and other institutions has resulted in the demolition of over 1,000 homes and apartments since 1950.

The West End, shown here in 1959, was demolished shortly after from 1960 and 1963 for Interstate 75 and the Queensgate industrial park. Photograph by Dave Tunison.
The Politics of Population Decline
A variety of unscrupulous local politicians and media figures cleverly play two sides of Cincinnati’s population loss narrative. According to them, Cincinnati has lost population due to high crime, high taxes, and corrupt city governance. But should the city start attracting new residents, the perceived “bad element” will be pushed outside city limits and into the areas of those trumpeting this false narrative.
Therefore, with every avuncular call for Cincinnati to improve itself, these figures work to undermine the city’s capital improvements, and have succeeded in creating a suburban culture that looks upon the city and those who support it with deep suspicion. What’s more, those who play the politics of decline know that Cincinnati cannot physically house 205,000 more residents without construction of dozens of hi-rise apartment blocks. Such apartment clusters and the subway system necessary to move their residents throughout the city would be met with excited accusations of “communism”.
Certainly, Cincinnati would benefit from new residents, especially in its under-populated neighborhoods where many historic structures are at risk of demolition. The arrival of 205,000 residents within the city limits would resolve many of the city’s current problems but would force higher apartment rents, increase noise and traffic congestion, and would motivate the demolition of historic structures for new multistory apartments and commercial buildings.
So while virtually every old American city has lost population within its city limits since 1950, some of that loss has occurred for reasons unrelated to the commonly heard decline narrative. Family sizes are smaller, non-residential buildings have been built in some former residential areas, and new neighborhoods have formed outside city limits to house those displaced by commercial and institutional growth. Considering these realities, the City of Cincinnati will likely never again be the home of 504,000 people, and so should not measure itself against its former peak population.