During a press conference this past October, superstar architect Frank Gehry responded to criticism of his work by raising his middle finger to a Spanish journalist and saying, “Let me tell you one thing. In the world we live in, 98% of what gets built and designed today is pure shit. There’s no sense of design nor respect for humanity or anything. They’re bad buildings and that’s it.”
Gehry’s sharp retort sparked a firestorm in the press; op-ed pieces in The New York Times, Forbes, Architect Magazine, and countless blogs have chimed in with their own responses, and the inevitable responses to the responses soon followed. Despite the brash way in which the conversation started, it is a conversation about our built environment that is welcome and long overdue.

The Inescapable Art
Blair Kamin, the Pulitzer Prize-winning architecture critic for the Chicago Tribune, described architecture as the inescapable art. “You don’t have to go to a play that the theater critic pans, a movie that the film critic hates or a restaurant where, according to the food critic’s taste buds, the chef can’t cook,” Kamin writes, but terrible reviews won’t make buildings disappear, and the public can be stuck with the consequences of bad design for decades. Architecture — good, bad, or mediocre — forms the setting in which we live out our lives and it affects us in profound ways whether we consciously realize it or not. Good design is more than just superficial window dressing; it’s the difference between Mac OS X and a Unix terminal prompt, and it’s the difference between a city that’s an attractive destination and a city that merely exists.
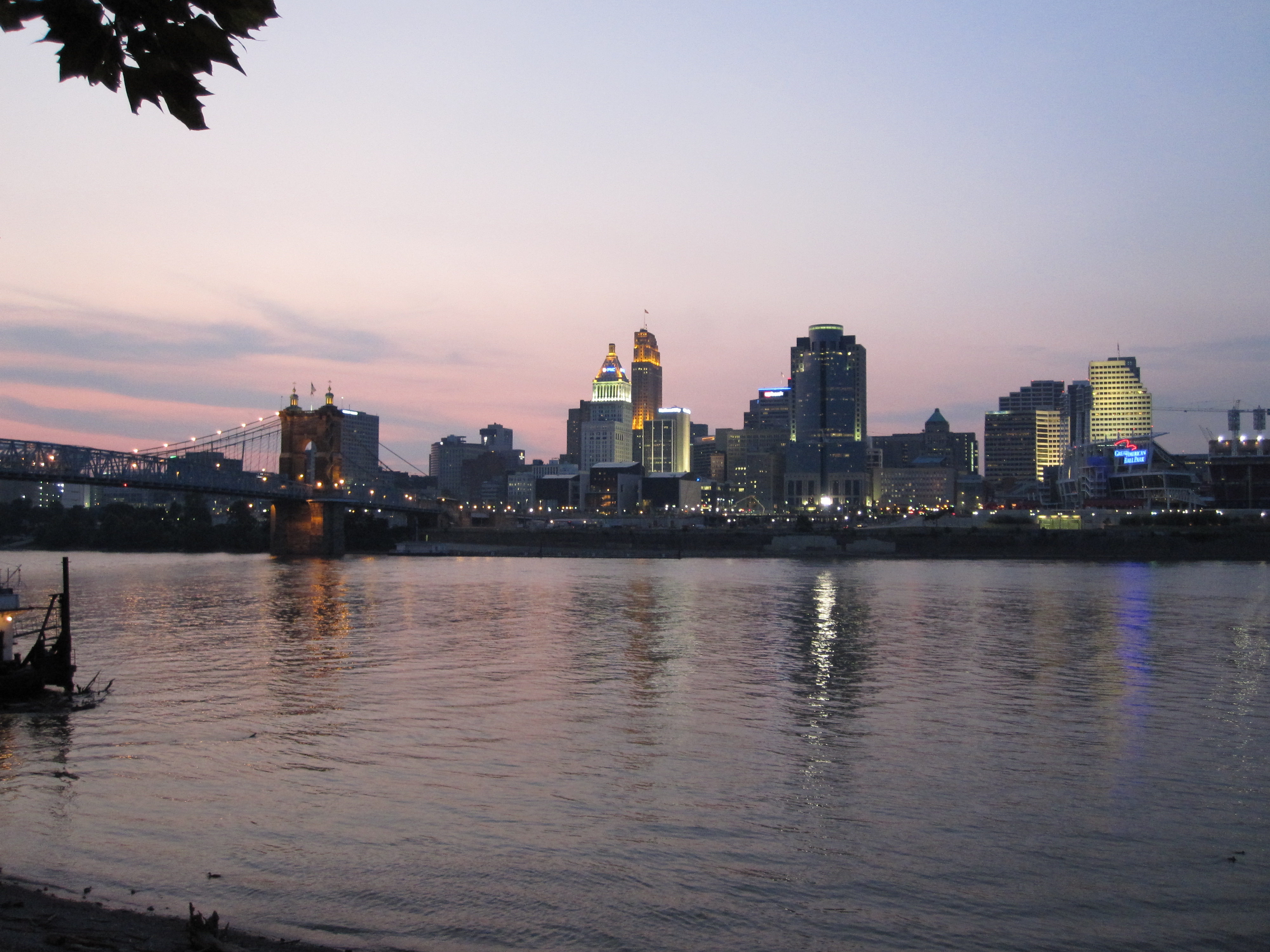
Cincinnati is blessed with a cornucopia of notable architecture that other cities in its league can only dream of having. In addition to the well-known favorites like Union Terminal, Carew Tower, and Music Hall, there is also a wide variety of contemporary architecture that has helped put Cincinnati back on the cultural map. In addition to the usual cast of flamboyant “starchitects” like Frank Gehry, Peter Eisenman, and Zaha Hadid, Cincinnati is also home to projects by less flashy but no less talented firms like Moore Ruble Yudell, Architecture Research Office, and Gwathmey Seigel Kaufman. There are also homegrown firms such as FRCH, Glaserworks, and John Senhauser Architects creating notable projects in Cincinnati and beyond. When it comes to the quality of its built environment, Cincinnati punches far above its weight.
The sad irony, though, is that relatively little of what gets built today is actually designed by architects. Despite the resurgence of the urban cores of Cincinnati and other cities throughout the country, most new construction is still in the suburbs and exurbs, planned and designed by developers and retail chains according to carefully-honed formulas created to guarantee the greatest return on the dollar within the shortest period of time.
Suburban “McMansions” aren’t designed by architects to be lived in; they’re designed by developers to look good on realtor listings and be sold. Big-box retail stores, fast food outlets, and car dealerships are built from prototypes designed not to inspire or to even be pleasant, but to generate short-term profits with maximum efficiency. Some nameless architect may have stamped the construction documents somewhere along the process to ensure the structure meets applicable codes, but his or her influence on the end user experience was likely minimal at best. In the case of most single-family houses built by developers, an architect was not likely to have been involved at all.
False Choices
This is no doubt the “98% of what gets built and designed today” that Gehry was referring to, but it has remained largely unmentioned while pundits squabble over the implications of his diatribe. Some commentators have chosen to blame celebrity architects such as him for the current state of our built environment, nostalgically harking back to some mythical past in which architecture was driven by the local vernacular. What they fail to mention is that, like it or not, badly-designed sprawl is the vernacular today, and it has gone global. Blaming a few starchitects for the quality of our built environment is like bashing Kraftwerk for being too esoteric while the latest Nickelback album is at the top of the charts.
That said, architects and architectural academics are often accused of being elitist and out of touch with reality, and in many cases the criticism is well-deserved. Too many architects have read Ayn Rand’s The Fountainhead as the manifesto it was meant to be rather than as the cautionary tale it should have been. Architecture is a collaborative discipline above all else, and there is no room at the table for an ego the size of Howard Roark’s. Too often, the prestigious design awards and glossy magazine articles have been for projects built for sheer spectacle rather than for lasting quality. Spectacle is what sells magazines and generates fodder for discussion around the water cooler, but sometimes the most appropriate design solution is to do less designing. Being a conscientious architect means knowing when to make that call.
What’s missing from the discussion is the vast middle ground between avant-garde starchitecture and crowd-pleasing vernacular design, and the idea that architecture, above all else, should be a human experience, rather than an abstract object to behold or a mere commodity to the bought and sold. It’s not a question of modernism versus traditionalism or suburban versus urban; it’s a question of bad versus good.
Healthy cities need an attractive mix of architecture; this mix includes high-profile starchitecture, anonymous background buildings, new and old, traditional and modernist, and everything in between. What matters is that what gets built is of consistently high design quality. A smattering of notable buildings within a context of ugly schlock is insufficient; what’s needed is a cohesive cityscape of well-designed buildings where the overall quality of the urban experience is greater than the sum of its architectural parts. To use a baseball analogy, one or two sluggers won’t save the season if the rest of the team is in a slump.
Good design doesn’t just happen; property owners and the general public need to realize its value, and commission talented architects who will deliver it. Samuel Hannaford didn’t leap out from behind a bush one night and create Music Hall by sheer force of will; Music Hall exists because the City of Cincinnati wanted a venue befitting its highest cultural aspirations, and they commissioned Hannaford to design it. Music Hall, while notable enough in its own right, also exists within the fabric of a historic neighborhood. Relatively few of the neighborhood’s Italianate row houses would be particularly notable as individual structures, but together they form the streetscape of Over-the-Rhine, one of the largest intact historic districts in the country. Music Hall and its surrounding neighborhood enhance and compliment each other in ways that would be impossible if either existed in isolation.

Cost considerations are often touted as an excuse for poor design, but this is a cop-out. It’s easy to clad a terrible building in exotic materials and pass it off as a notable work of architecture (see: numerous projects developed by Donald Trump), but a talented architect can creatively turn cost constraints into a brilliant design solution.
The iconic cross-braces on Chicago’s John Hancock Center meant being able to eliminate a third of the structural steel that would’ve otherwise been required for a building that tall. At a much smaller scale, Auburn University’s Rural Studio designs hand-built structures of sublime beauty for disadvantaged communities in rural Alabama. These structures, often created from recycled materials and found objects, cost pennies on the dollar compared to more typical construction.
When Washington, DC was planning its Metro system, the transit authority assumed the cheapest way to construct the underground stations was to give them straight vertical walls covered in tile, flat ceilings, and a forest of columns similar to what’s found on older subway systems. Their architect, Harry Weese, was able to demonstrate that a vaulted station shell made of waffle-slab concrete actually cost less to build than a more conventional design. This motif became the most celebrated design feature of the system, subtly recalling the coffered ceilings of the District’s neoclassical civic monuments but without reflexively copying them.
What is Good?
All this talk of good architecture begs the question: What does it mean to be good? Is it something that can’t be defined, but we know it when we see it? Aaron Betsky, former director of the Cincinnati Art Museum and now Dean of the Frank Lloyd Wright School of Architecture, recently penned an article that explicitly addresses this question:
I do not think there is one style or one approach that has all the answers. I am wary of what I think are pseudo-scientific approaches to measuring such things, though I am open to ways in which we can more clearly articulate and judge what is good and what works. However, instead of taking solace in formulas or a rote recitations of traditions, we should always ask the question what is appropriate, what is needed, what is possible, and what are our dreams and aspirations. We should build with what we know, for a reality, but also towards a better — again in a social, environmental, and aesthetic sense — reality.
Betsy concludes the article by saying, “Architecture should be neither weird nor boring, neither alien nor alienating, neither wasteful nor wanting in the qualities that make us human.”
To this we might add: In order to be good, architecture should be honest in its materiality and its place in history, and be responsive to its context. Wood should look like wood and not be painted to look like marble. A building built in 2015 shouldn’t attempt to look like a building built in 1895. A sentimental appeal to nostalgia is no excuse for faux-traditional buildings that cheapen their context with knee-jerk imitation, but a building designed for downtown Cincinnati should be sufficiently distinguishable from a building designed for a suburban office park in Southern California.
Good architecture should engage all the senses in a meaningful way, and acknowledge the web of meanings and experiences that we have come to associate with the built environment. Brick is more than just a cladding material; it imparts a sense of stability and permanence. Glass and stainless steel are associated with notions of high-tech precision. A fireplace is more than just a decorative feature in the living room; the sound and smell of burning firewood recalls fond memories of family camping trips, a bonfire on the beach during a church retreat, or a brisk fall evening with close friends on the patio at Neons. A door made of solid wood has a more substantial feel to the hand than a flimsy hollow door made of pressed paper, even if they both look the same at first glance. Whether we are consciously aware of them or not, these things matter.
Local Interest
The discussion about the nature of our built environment has been happening in Cincinnati for quite some time; debates about the streetcar, gentrification, redeveloping the riverfront, form-based codes, and historic preservation all revolve around what kind of place Cincinnati wants to be. Is it a place where one merely goes to see a Reds game once or twice a year before getting back on the freeway to a house in the suburbs, or is it a place to live and work 24/7 throughout the year? Is it a dumping ground for the indigent, a playpen for the affluent, or home to a diverse mix of people and activities? All these issues are closely related to matters of design.
The Cincinnati Enquirer recently published an angry screed by Hyde Park architect Robert-Pascal Barone that sharply criticizes a number of recent projects. Although the article contained a few valid points, the overall tone read as a shrill rejection of anything built in the city after 1950, which undermined the possibility of a constructive dialogue.
This was an unfortunate missed opportunity, because it’s a dialogue that needs to happen. Belligerent naysaying does nothing to improve the city, but even the most successful projects are not exempt from intelligent critiques that offer lessons for future projects. Cincinnati has progressed beyond the point where new development for the sake of new development, no matter how ill-conceived, should get the red carpet treatment by default. The city deserves top-shelf design, and is now in a position to demand it.
Moving Forward
There is reason to be optimistic that we are once again making good architecture a priority. For the past 20 years, the University of Cincinnati’s Signature Architect Program has raised the profile of the university and has led to UC consistently appearing on lists of the world’s most beautiful college campuses. More importantly, it has greatly enhanced the quality of campus life and has had a snowball effect on other projects around town.
In recent years the city has stepped up its efforts to save and preserve the architectural landmarks that previous generations have built. The dilapidated Metropole has been beautifully reborn as the 21c Museum Hotel, Hamilton Country taxpayers recently approved a modest sales tax increase to restore Union Terminal, and the long-awaited restoration of Music Hall continues to gain support and funding.
Much work remains: the Terrace Plaza Hotel still sits vacant downtown, and despite the pace of redevelopment in Over-the-Rhine and other close-in neighborhoods, each year sees a number of vulnerable structures succumb to neglect or outright greed. The city needs to be more proactive about preserving its history, rather than merely reacting when a problem becomes a crisis.
Smaller cities like Cincinnati have a unique role to play in the design world, and offer advantages of access and affordability not found in the usual hot spots like New York and San Francisco. In a recent CityLab article titled Why Architects and Second-Tier Cities Need Each Other, Amanda Kolson Hurley notes:
New York, Boston, Chicago, and other major metros have a lot of construction activity, but also a lot of architects. It’s a competitive field made more so by the sheer number of talented firms in the same handful of cities. That contributes to the culture of stress and overwork that many architects bemoan, some of them — women in particular — even leaving the field in frustration. By contrast, an ambitious architecture practice can carve out a niche for itself in a second-tier city, where the scene is often dominated by “legacy” firms that play it safe.
Hurley goes on to highlight the example of Louisville-based De Leon and Primmer Architectural Workshop, which recently won an AIA Honor Award for their Wild Turkey visitor center in Lawrenceburg, Kentucky. Neither Roberto De Leon nor Ross Primmer are Louisville natives; they met in architecture school at Harvard and made a business decision to open their practice in Louisville because, like Cincinnati, it was primed for growth. Cincinnati has the additional advantage of being home to one of the top architecture schools in the country, and many faculty members have their own small practices producing innovative design.

Most importantly, the general public needs to demand a consistently high standard of design and hold its leaders accountable when opportunities are missed. Uncritical boosterism is often a veneer for complacency, which is a far more destructive force than vigorous debate. Sometimes the boat needs to be rocked. Cincinnati has a rich history and enviable assets, but it cannot rest on its laurels. No city has ever made itself a prime destination by bragging about how magnificent it used to be.
Get Involved
At the national level, the American Institute of Architects has launched an ambitious media campaign to highlight the role of architects in shaping our built environment, and by extension, the role of the built environment in shaping our lives. The campaign features web videos, television ads, and social media content under the hashtag #ilookup.
For those wishing to become more involved in conversations about the future of Cincinnati’s built environment, the Cincinnati chapter of the AIA and the Architectural Foundation of Cincinnati have full calendars of activities and events, and the annual ArchiNATI festival offers unique opportunities to engage with the city’s built environment.
In addition to the University of Cincinnati’s College of Design, Architecture, Art, and Planning, other nearby architecture schools at Miami University, the University of Kentucky, and Ohio State University routinely host lectures and other events throughout the year that are usually free and open to the public.
If all that sounds daunting, start by simply grabbing a sketchpad and heading off to explore some corner of the city that looks interesting. Look up, and you’ll rarely be disappointed.
[youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JLhbTGzE6MA&w=640&h=360]
David Cole is a native of Fort Thomas, Kentucky with a strong interest in architecture, urban design, transit, and social justice. He earned his Master of Architecture degree from the University of Cincinnati’s College of Design, Architecture, Art, and Planning, and is pursuing professional registration as an architect while working as a designer at the New York office of STUDIOS Architecture.
If you would like to have your thoughts published on UrbanCincy, simply contact us at editors@urbancincy.com.