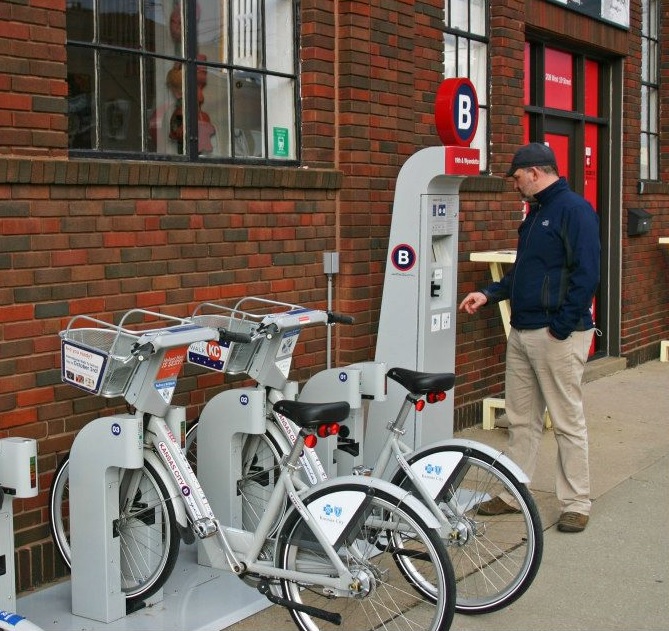
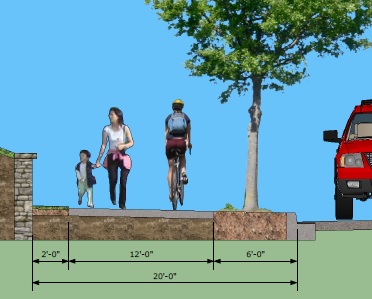
The City of Dayton, in collaboration with Bike Miami Valley, Downtown Dayton Partnership and the Miami Valley Regional Planning Commission (MVRPC), plans to start a bike share program in the spring of 2015.
The City of Dayton, in collaboration with Bike Miami Valley, Downtown Dayton Partnership and the Miami Valley Regional Planning Commission (MVRPC), plans to start a bike share program in the spring of 2015.
The system will operate similarly to Cincinnati’s planned bike share system announced this past February. The main difference between the two, however, is that Dayton has secured $1 million in capital funding to build out the initial system of more than 200 bikes and 22 stations located throughout Dayton’s center city.
According to city officials, the bulk of the capital funding will come from a grant from the Federal Highway Administration Surface Transportation Program. The City of Dayton will then provide an additional $250,000 funding for capital costs and initial operations.
The accomplishment of securing the capital funding was one not lost on those at the press conference. Scott Murphy, director of business development at the Downtown Dayton Partnership, emphasized that Dayton is the second city in Ohio to secure the capital for a bike share program.
Even though Cincinnati officials have yet to secure the capital funding for their planned bike share system, they remain optimistic they can do so and start operations in 2014 – ahead of Dayton’s planned launch early next year.
Also unlike Cincinnati where a non-profit entity will manage the system, the Greater Dayton Regional Transit Authority will take the lead in managing the program, and in selecting an operator. According to Executive Director Mark Donaghy, a request for proposals will be issued in the next three months, and an operating contract will be awarded this summer.
Dayton officials estimate that the infrastructure will be delivered this coming winter, with the program becoming operational in the months thereafter. Bike Miami Valley, a local cycling advocacy group, spurred the whole effort to bring bike share to Dayton with the preparation of a feasibility study.
Findings of the study indicated that Dayton has a higher level of suitability for a program than some similarly sized cities that already have bike share, such as San Antonio, Chattanooga and Madison, WI. The study also estimated that Dayton’s system would handle approximately 50,000 to 70,000 annual bike share trips.
Local leaders are giving the program enthusiastic support.
“Bike share is a natural extension of our transit system,” stated Donaghy, who went on to say that the RTA was the first transit system in Ohio to equip its full fleet of buses with bicycle racks.
Such efforts to embrace bicycling have made Dayton a bronze level Bicycle Friendly Community, as rated by the League of American Bicyclists. Community leaders in Dayton, however, intend to become reach the platinum rating by 2020.
Brian Martin, Executive Director of MVRPC, stated that the program will expand and enhance existing services of the Regional Transit Authority, while also helping reduce auto dependency. In part due to the study conducted by Bike Miami Valley, and the tangible changes taking place in Dayton’s center city, local leaders say they knew this was the right decision.
“The number of housing units in downtown Dayton has doubled in the last 10 years,” Dayton Mayor Nan Whaley told UrbanCincy. “We know this is what people want.”