Cincinnati is exploring the idea of implementing bus rapid transit (BRT) lines to create better transit access from the city’s inner-ring suburbs to the employment centers of downtown and uptown. The success of BRT is often determined before the first passenger ever boards. Design, routing and operation planning often determines the level of success experienced. As a result, UrbanCincy traveled to Bogota, Colombia to see how one of the world’s most famous, and successful bus rapid transit systems works.
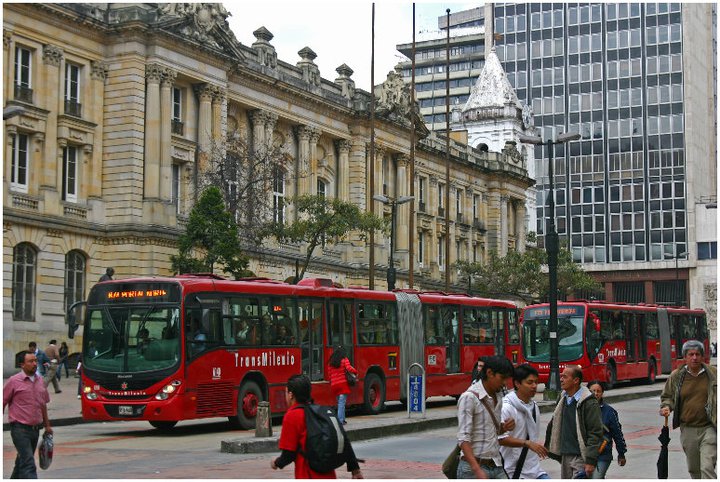
Bogota’s TransMilenio system first opened in December 2000. The investment was made in lieu of a much more expensive, and invasive, highway building project to relieve congestion in Colombia’s largest city. Since that time, the TransMilenio’s reach has grown along with its popularity, now serving 1.5 million riders each day along its nine lines totaling 54 miles.

TransMilenio Peppe Sierra Estacion on Bogota’s north side. Photograph by Randy A. Simes.
Design
The TransMilenio operates in the center of major thoroughfares throughout Bogota. Riders often access the stations by crossing steel walkways that extend over the wide streets below. The stations also use similar steel framework and include glass doors that open when buses pull up to the platform.
The simple design helped to keep initial costs low ($9.6M per mile), but is showing signs of significant wear and tear. The open air stations also suffer from the extreme pollution from vehicle, truck and bus exhaust along the busy roadways.
The buses themselves are typically single-articulated red buses that are easily recognizable from the city’s plethora of private buses operating as circulators throughout the rest of the city. To accommodate more passengers, new double-articulated buses are now being integrated into the overall system as station design permits.
Routing
It is important to note that the TransMilenio only operates along major thoroughfares and functions much like an above-ground rapid transit system. The buses do not reach into neighborhoods and instead focus on moving people long distances along specific corridors. Other trips are better made by using the small, private buses operating on local streets.
The original TransMilenio lines were routed much like those being planned for Cincinnati. Lines focused on moving people from heavily populated residential areas to the downtown business district, surrounding university and government buildings, and tourist attractions. New lines are extending into secondary job centers including the city’s international airport.


TransMilenio BRT service in downtown Bogota along Calle 13 [LEFT]. Service doors at Avenida Jimeniz TransMilenio Estacion in downtown Bogota [RIGHT]. Photographs by Randy A. Simes.
Operations
The TransMilenio may be one of the most sophisticated BRT systems in the world. During peak travel times, buses operate at extreme frequencies with buses arriving at station platforms virtually non-stop. The buses also receive traffic light priority. They are not timed with lights due to the unpredictability of station length stops as passengers try to cram on the bus.
The system operates from 5am to 11pm and uses an electronic fare payment system. This payment system is different from others systems around the world. Riders purchase a specific number of trips from a person staffing each location. This creates backups during heavy travel times as many people attempt to purchase trip cards. These cards are then used until the last trip when the card is inserted into the turnstile and recycled for later use.
Fares have risen steadily since the system began operation in late 2000, and now costs 1,700 Colombian Pesos per trip (about $1). The huge ridership numbers clearly allow for fares to be kept low, but the rising cost of oil is sure to impact a system that relies solely on diesel fuel.
The buses are all managed at a central dispatch center which tracks average travel speeds, stacking at stations and other schematics. This system tracking allows operators to determine how future improvements should be made, and how operation changes can improve service.
Conclusion
Cincinnati should learn from Bogota’s experience. The TransMilenio offers superior service, but also suffers from problems that could be solved with a greater upfront investment.
When operating lots of big buses at high frequencies, it is no wonder that heavy pollution comes with it. Bus rapid transit in Cincinnati should utilize electric overhead wires, or some sort of clean fuel technology to prevent such pollution from proliferating along the lines.
When designing bus rapid transit lines and stations for Cincinnati, city leaders and transit officials should not view BRT as a cheap transit alternative. In the case of BRT, like many things, you get what you pay for. The TransMilenio has robust stations and huge amounts of right-of-way clearly separated from other traffic. BRT systems that do not invest in superior station designs and separated right-of-way, will suffer lower ridership due to the lack of improved travel times and overall perception problems.
Bus rapid transit should also not be viewed as a transit solution to be done instead of rail investments. This has been seen in Bogota, and city leaders there are now working on a new subway and a massive light rail system that will compliment the TransMilenio which will eventually cover 241 miles.