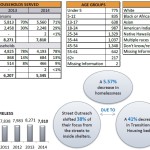
A newly released report shows that homelessness in Cincinnati and Hamilton County declined in 2014 to levels not seen since 2010.
The report comes from Strategies to End Homelessness, a local leader of 30 homeless service organizations. Using data from the Homeless Management Information System, the non-profit organization said that they saw positive results all around.
The number of people on the streets, which saw a large jump in 2013, returned to 2011 levels. Those staying in emergency shelters also dropped by 7% since 2012, which officials say can be attributed to the increase in people being served by permanent housing programs, which has increased 167% since 2010.
Local leaders also say that this drop is also partially a result of their member organizations’ homeless prevention efforts, which Kevin Finn, CEO of Strategies to End Homelessness, told UrbanCincy in March is one of the most critical factors in reducing homelessness.
Since 2011, these organizations have seen only 10.2% of the people served by their shelter diversion programs later become homeless. Finn says that preventing people from needing a shelter is not only effective, but it saves money as well.
“Homelessness prevention activities work and at a fraction of the cost of assisting after a person is already homeless,” said Finn. “Stopping people from ever needing to enter a homeless shelter just makes sense.”
The report found that men make up 59% of Cincinnati and Hamilton County’s homeless population, and that some 66% of those that are homeless are black.
One of the national trends is that women and children make up one of the fastest growing segments of the homeless population. In Cincinnati and Hamilton County, the report found that children are 29% of the area’s homeless – 6% of which are children without adult accompaniment. Furthermore, approximately 15% were found to be veterans.
In all, the number of people on the streets, in shelters, or in transitional programs in all of Hamilton County was 7,810 in 2014.
The Cincinnati area received a U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development grant of $15.4 million earlier this year to combat homelessness. This money has not yet been distributed, but once it does, it will be set aside for non-prevention programs.
Local leaders also have reason to be optimistic due to the ongoing investment in new facilities, through Cincinnati’s Homeless to Homes program, to care for the area’s homeless population.
“In 2015, three improved shelters are opening, significantly improving the quality of services being offered to the homeless in our community,” Finn said. “We are also hoping to expand prevention efforts, so that fewer people will have to experience the trauma of homelessness.”