Shortly after breaking the news that The Banks development team is in negotiations with AC Hotels to bring the trendy European hotel brand to the central riverfront, UrbanCincy confirmed that the real estate development arm of Western & Southern is close to finalizing an agreement that would bring a boutique hotel to Lytle Park as well.
Multiple sources have confirmed that a deal is being worked out that would bring an Autograph Collection hotel to the former Anna Louise Inn. When reached for comment, Mario San Marco, President of Eagle Realty Group, acknowledged that the company is working diligently to bring an Autograph Collection hotel to the site, but that details had not yet been finalized or presented to City Hall.
Western & Southern executives had previously stated that they wanted to bring a boutique hotel to the site that would have somewhere around 106 rooms. The plan would fit the company’s larger plans for the historic district that call for creating a high-end enclave surrounding Lytle Park, which Western & Southern helped save from demolition in the 1960s by pushing for the creation of Lytle Tunnel.
Autograph Collection is a unique brand owned by Marriott International. Instead of the rest of their brands which maintain their names, Autograph Collection makes a unique name and concept for each of their sites. The closest such hotel is Cleveland’s 156-room Metropolitan at The 9.
Sources have also confirmed that, like the AC Hotel at The Banks, this boutique concept by Autograph Collection would be managed by Cincinnati-based Winegardner & Hammons.
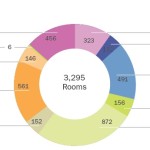
The two recent hotel announcements appear to be the end of the center city’s recent hotel boom that has included a new 122-room SpringHill Suites, 134-room Residence Inn by Marriott, 160-room 21c Museum Hotel, 323-room Renaissance Hotel, 105-unit Homewood Suites, 144-room Hampton Inn & Suites, and a 144-room Aloft Hotel.
The boom has also included major, multi-million dollar renovations of the Hyatt Regency and Westin Hotel in the heart of the central business district. The remaining unanswered question continues to be what will happen with the deteriorating Millennium Hotel, which, at 872 rooms, is the center city’s largest, and serves as the region’s primary convention hotel.
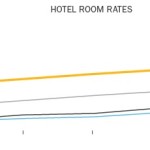
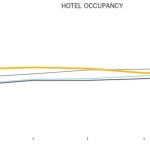
Despite the addition of more than 1,100 new hotel rooms over the past several years, occupancy rates have held relatively constant. More critically, room rates and RevPAR – the hotel industry’s calculation of revenue per hotel room – have been steadily increasing over the same period and are now well above regional and national averages.
Project leaders at Eagle Realty Group declined to provide any specific timeline or budget for the project, but previously stated that they hope to get an operator under contract by mid-2015, with construction commencing shortly thereafter.