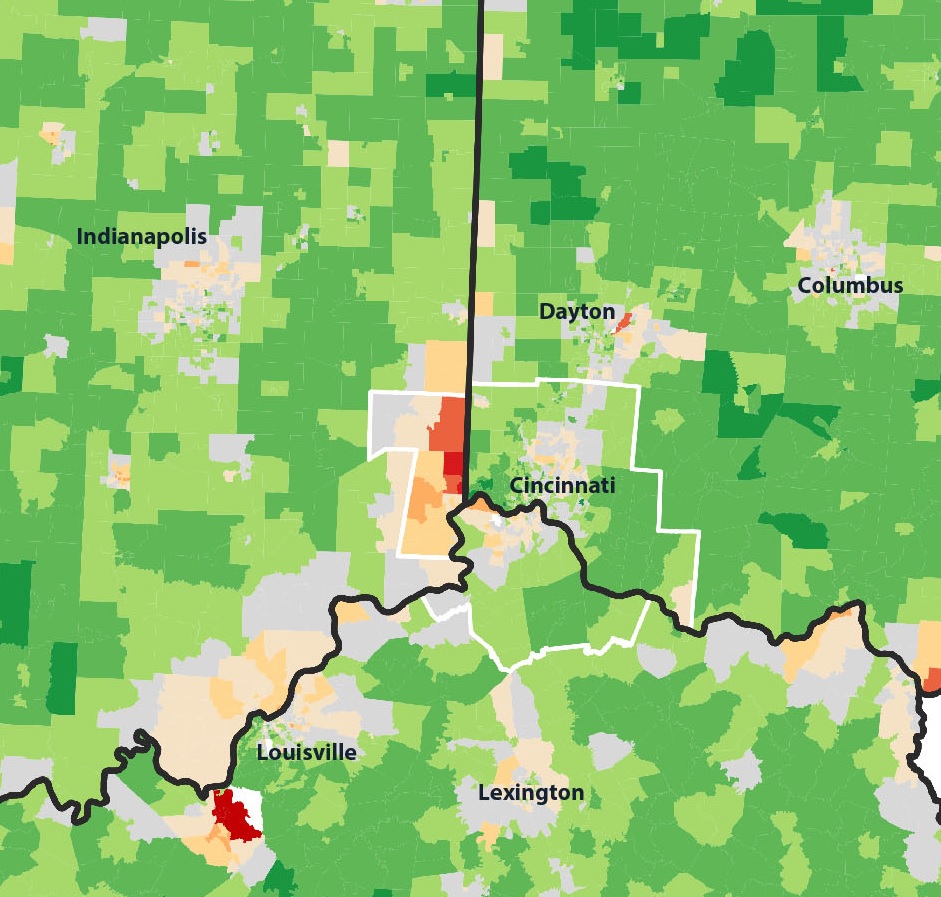
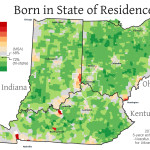
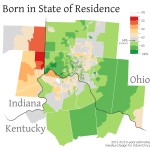
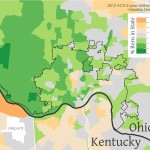
For the first time there are no grocery stores in College Hill, Northside or Clifton. At one time each neighborhood had their own store including a Kroger in College Hill, IGA in Clifton and Save-A-Lot in Northside.
When Save-A-Lot closed its Northside store in November 2013, however, it got the attention of the Cincinnati Union Coop Initiative (CUCI) and sparked an effort to open a community-owned grocery store in its place called Apple Street Market.
There is only one full-service grocery store within a three-mile driving distance from Northside – a Kroger on Mitchel Avenue. That Kroger, however, is not served by Metro’s #17 bus route, thus leaving carless households with only Metro’s #16 route as their option. The problem is that the #16 bus route does not run on Sundays and only runs every half-hour after 4pm.
“This makes a grocery trip an arduous and time consuming journey if you do not have a car,” said Casey Whitten-Amadon, legal counsel for Apple Street Market. “The trip can take more than three hours, in all types of inclement weather.”
It was the closing of the Save-A-Lot, however, that really sparked the effort to open a new community-owned grocery store in Northside.
“I knew that CUCI had been starting worker owned ventures. So, I approached them about a grocery store within the first week of Save-A-Lot closing,” said Heather Sturgill, a Northside resident and community advocate.
CUCI did a lot of searching to find the best fit for the new store. They were not specifically tied to Northside, but after surveying about four different neighborhoods, along with conducting market studies and market analysis for grocery stores, they found Northside to be the perfect fit. One of the key reasons for this, they say, is that Northside had an existing space that was in great shape and needed little to no demolition or remodeling.
This was important, and stands in contrast to the ongoing difficulties Clifton is having in trying to open their own cooperative grocery store on Ludlow Avenue, because they did not have the capital nor did they have a large investor that would finance the project.
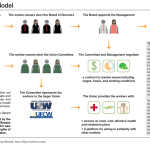
This is particularly complicated by the financial model of union co-op businesses, where a large investor cannot have a larger share of the profit or a larger share of the governance rights. Rather, each person or entity that invests in the store gets an equal share and one vote regardless of the investment.
In the case of Apple Street Market, CUCI is accepting $100 or $10 from lower-income investors.
While raising the capital for a union coop startup can prove to be extremely difficult, Northside’s effort has been aided by a large number of enthusiastic volunteers that also set the community apart from others in the city.
While this collection of neighborhoods represents a relatively new and small food desert in Cincinnati, it comes at a time when many policy makers are looking to fix such problems.
“This is another reason that we decided to go ahead with the project in Northside,” said Whitten-Amadon. “The main benefit to community ownership is the opening of a unique store that is owned by the workers and the community.”
He also says that success and profitability will be shared by the community, and that being able to make decisions collectively will help create a sense of pride in the neighborhood store.
While community leaders are excited about the potential benefits for the community investors and workers, they are also looking forward to the local specialty items that will be stocked at Apple Street Market. Organizers say that the plan is to provide a larger than average organic and produce section, and sourcing much of it from Our Harvest – another area worker-owned business started by CUCI.
But Sturgill says that they will also be including up-and-coming brands to give the store an affordability that most health food cooperatives do not have.
“We tried to get fresh foods in some of the other corner type shops but the owners didn’t seem interested enough to follow through,” Sturgill told UrbanCincy. “This is intended to be the first in a chain of worker/community owned groceries.
A future additional location for this type of store, she says, could be in College Hill at the new development planned for North Bend Road and Hamilton Avenue.
An official opening date has not yet been set for Apple Street Market, but Sturgill says the goal is to have it completed by spring 2015. Those who are interested in providing funding and making an investment in the store can do so by buying a share online.