Last week Cincinnati City Council approved the form-based code for Walnut Hills. The unanimous vote marks the third neighborhood to adopt this new regulatory tool for neighborhood redevelopment. Yet even after several years of development, many do not understand the basics about the new land use planning tool.
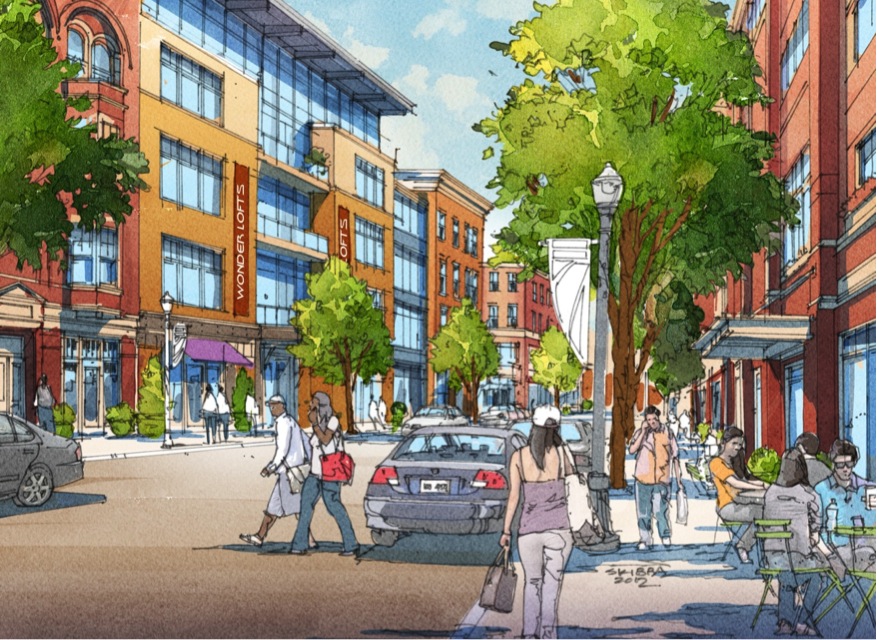
First of all, a form-based code is type of regulation that is developed by community stakeholders to guide future development or redevelopment of a community. Under a form-based code, new developments are typically configured to mesh with the character of the community’s vision.
Form-based codes get their name because it creates a type of regulation that typically focuses more on the form of the building and its relation to the public realm (i.e. the street) rather than the usage of the building. Development under the code occurs “by-right” and means if a new development complies with all the code’s provisions it can be built without having to go through the extensive and sometimes drawn-out process of traditional development.
Over 700 American cities have adopted some type of a form-based code, with Miami being the largest city to completely adopt this type of code. Near by they have been used in Nashville and Columbus to spark development in revitalizing areas of their inner cities.
Former Vice Mayor Roxanne Qualls (D) championed this movement locally and actually led groups of local officials and business leaders to Nashville to study the results of their form-based codes in 2008 and 2012.
While some cities have used these tools to encourage pedestrian friendly, mixed-use developments where none exist, older more established cities such as Cincinnati have opted to implement them in order to ensure that new development integrates seamlessly into the historic charm and character of the city.
Bellevue, KY became the first municipality in the Cincinnati region to adopt this type of regulation in 2011.
Cincinnati first began pursuing the idea of developing a form-based code in 2009. After receiving funding through the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, city staff selected Opticos to lead in developing the new code. Dan Parolek, principal of Opticos, wrote the book on form-based codes, quite literally.
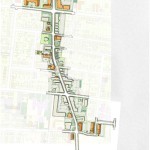
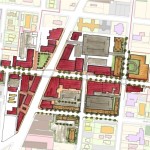
After conducting a city-wide charrette in May 2012, the City of Cincinnati worked with Opticos to refine the code and prepare it for adoption. The form-based code was adopted in early 2013. From there staff from the city’s planning department worked closely with neighborhoods to craft the regulating plan map.
Four neighborhoods were included in the initial implementation schedule: Madisonville, College Hill, Westwood and Walnut Hills. Both Madisonville and College Hill have fully adopted the code with Walnut Hills being the latest. Westwood appears to be the next neighborhood poised to adopt the code after winning unanimous support from the city’s Planning Commission in December 2013.