On Tuesday April 24 and Wednesday April 25 residents will have a chance to voice their concerns about the preferred Brent Spence Bridge design alternative, currently known as Alternative I at Longworth Hall. The proposal would build a new bridge adjacent to the existing Brent Spence Bridge.
The process, which began in 2004, has a nebulous future ahead of it with uncertainty pertaining to future funding from a new federal transportation bill. Recently, state officials have said that parts of the overall rebuild of I-75 through Cincinnati may be delayed for up to fifteen years. The new funding paradigm has left local leaders on both sides of the river talking about public-private partnerships. Because of this uncertain future, it may be possible to reexamine one of the bridge options not pursued.

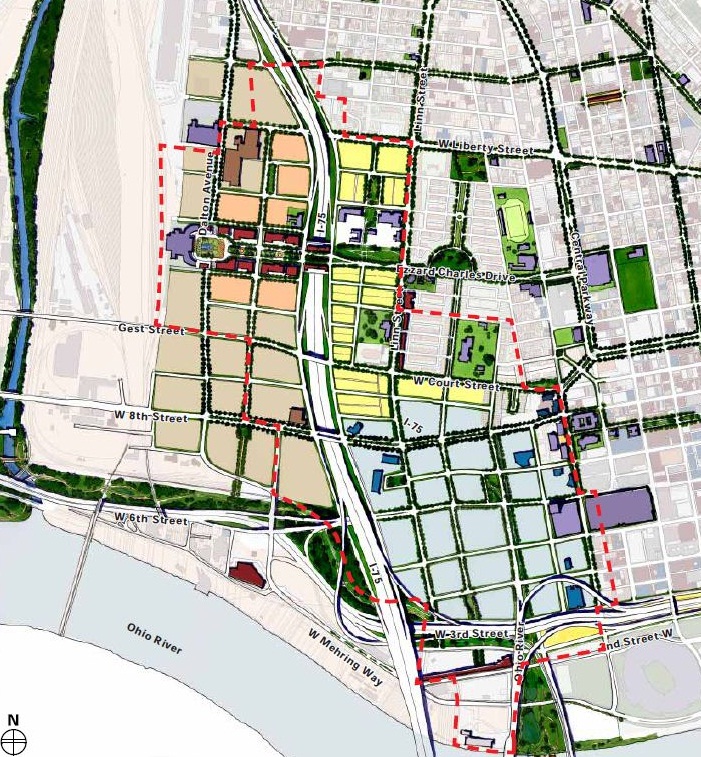
More than two dozen new city blocks would be able to generate in excess of $200 million annually in property tax revenue alone, should the new Brent Spence Bridge be shifted west. Rendering from Revive I-75 Study.
In 2010, the City of Cincinnati hired consultants to conduct several workgroups along the Interstate 75 corridor within the city limits. The study, named Revive I-75, addressed ways to mitigate the impact of the expanded highway on the surrounding urban neighborhoods. What also came out of the study was a visualization of the possible configuration of a new bridge for I-75 on the opposite side of Longworth Hall that would have allowed for the expansion of the Central Business District.
At the time there were several alignment configurations under study that would have moved the new bridge west of Longworth Hall, shrinking the amount of land the spaghetti-like on ramps use to connect I-71 to I-75 and the bridge. These alternatives were embodied in Alternatives A & B in the Brent Spence Bridge Corridor study. Yet both alternatives were removed from consideration citing environmental impacts and cost concerns. One of the arguments raised in opposition to the proposal was that that the city would lose valuable tax revenue from the affected industrial businesses in Queensgate.
However; according to urban economists such as Joe Minicozzi and Peter Katz, multi-story mixed use development actually brings in the most tax revenue for local jurisdictions when compared to single use facilities. In their study on Sarasota, Florida, it was found that a local mall generated only $22,000 in tax revenue per acre whereas a 17-story mixed use tower generated $1.01 million in tax revenue per acre. Since the 2010 study, Minicozzi has performed the same study in over fifteen different municipalities with similar results.
In a recent article written by Emily Badger, she summarizes several pertinent studies and surmises that, “We tend to think that broke cities have two options: raise taxes, or cut services. Minicozzi, though, is trying to point to the basic but long-buried math of our tax system that cities should be exploiting instead: Per-acre, our downtowns have the potential to generate so much more public wealth than low-density subdivisions or massive malls by the highway. And for all that revenue they bring in, downtowns cost considerably less to maintain in public services and infrastructure.”

Shifting the new Brent Spence Bridge to the west would allow downtown Cincinnati to be relieved from the existing and proposed entanglement of highway ramps. Rendering from Revive I-75 study.
A land use analysis performed by the UrbanCincy team found that the alternatives presented and illustrated in the Revive-75 documents would increase the amount of new land available in the Central Business District by roughly 33 percent. Approximately 25 new city blocks would be created under the proposal, freeing up land that is currently taken up by the expansive tangle of roadways that connect I-75, I-71 and the Brent Spence Bridge.
This would be accomplished by maintaining the ramps that connect I-71 to the Brent Spence Bridge and extending Fort Washington Way west, becoming the Third Street Expressway. This expressway will later align with the Sixth Street Expressway after connecting to the new bridge alignment west of Longworth Hall. The street grid would then be reestablished and developable real estate could be maximized on the newly reclaimed land. Based on the research provided from Minicozzi and Katz, UrbanCincy estimates that the taxable revenue capture could be more than $200 million from property taxes alone.
Such a move would not only allow for a sizable expansion of the Central Business District, but it would also create available land for a future expansion of the Duke Energy Convention Center. In a time when public agencies are trying to do more with less, this is a perfect opportunity to create more tax-productive property in the heart of the Cincinnati region. Moving the new bridge west is a solution that city, county and local business leaders should all support.