Recently, the Cincinnati City Planning Department sent out a notice to property owners in downtown and Over-the-Rhine regarding the implementation of an Urban Parking Overlay District. The city will hold several meetings with the next one being at the City Planning Commission meeting this Friday, July 27th at 9 a.m. If approved, the district would remove the requirement for uses in downtown to provide off-street dedicated parking.
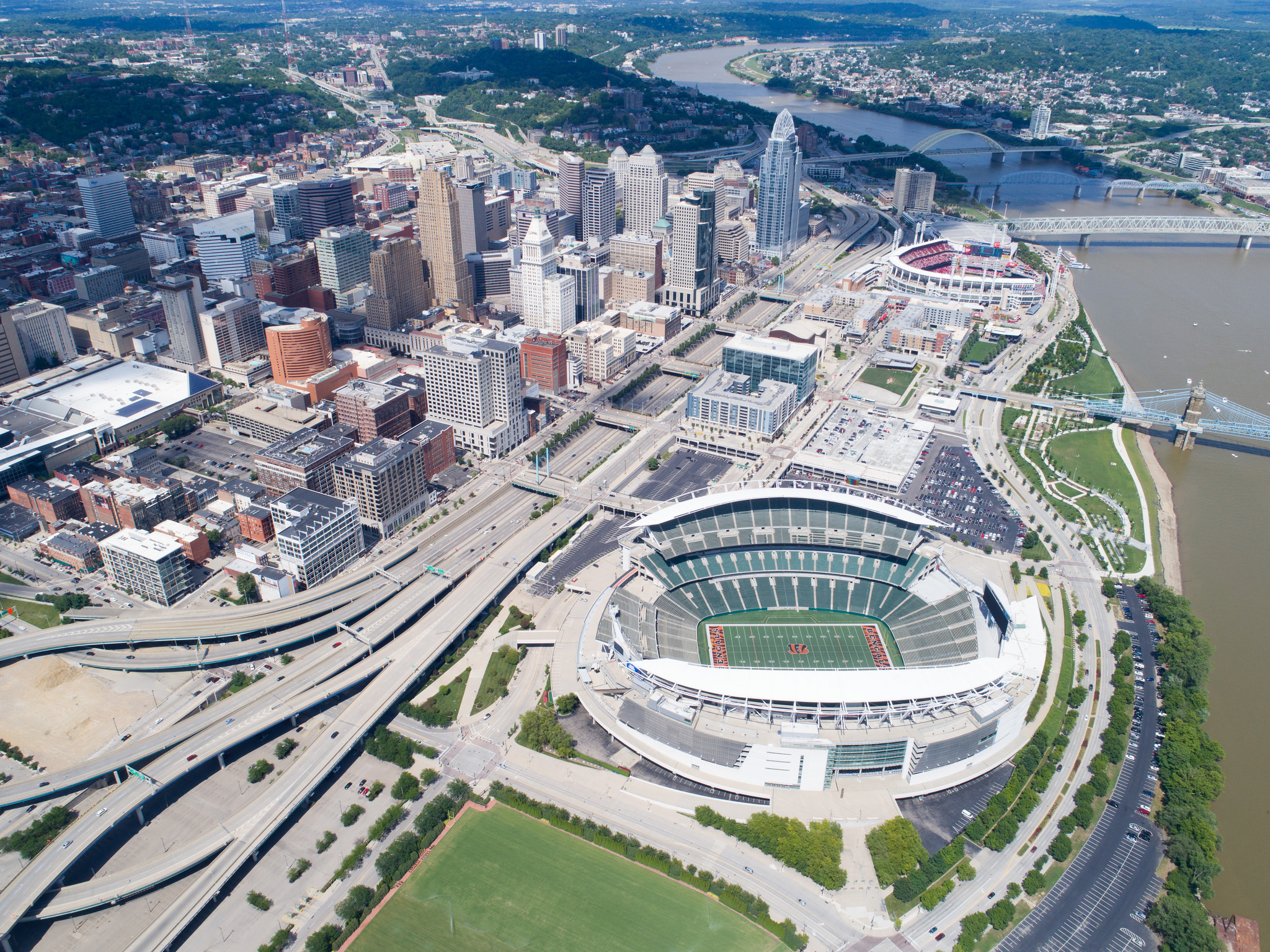
Since 2012 when I first wrote about parking in downtown and Over-the-Rhine the number of off-street parking supplied has increased well over 3,000 parking spaces (38,760 in downtown alone according to DCI). The Banks parking garage alone with over 6,000 spaces is the third largest parking garage in the United States.
We have an abundance of parking in the urban core.
At its core function, the removal of required parking minimums has proven to allow for more creative parking solutions to blossom. As Donald Shoup, parking guru and professor at UCLA found in his book The High Cost of Free Parking, most parking minimums were established as arbitrary standards by planners in the middle of the last century. Many of these requirements are intended to account for the busiest times of the day or year. UrbanCincy interviewed Dr. Shoup in 2014 regarding a variety of local parking issues.
In Nashville for example, the removal of parking minimums helped remove barriers for small-scale developers who could not afford to acquire additional land for a few parking spaces. Instead, agreements with nearby garages helped facilitate automobile storage demands.
Back in 2012 Nashville Planner, Joni Priest told UrbanCincy, “Removing the parking requirements from downtown zoning allows flexibility for site-specific and program-specific solutions. Flexibility is key in urban environments,” said Priest. “As downtown becomes more comfortable for pedestrians, cyclists and transit users, new development will have the flexibility to build less parking.”
Meanwhile, in Cincinnati, the city continues to struggle with developers looking to build new infill or rehabilitate and reactivate the many historic buildings in the urban core.
Even when parking requirements are reduced or eliminated most banks and investors still require parking to be provided or identified for developments to move forward. Removing zoning requirements for parking often allows the developer to build the parking that is really needed and not what is arbitrarily demanded by local zoning controls. This reduces the cost of development and in turn, allows more affordable housing to be provided.
Removing parking minimums also preserves historic structures from being demolished for parking lots and garages. Over-the-Rhine is the largest collection of German Italianate buildings in the country yet it currently has lost over half of its historic structures. If parking minimums are retained, the demolition of our communities historic assets will continue to be encouraged to meet the city’s parking requirements.
There is an abundance of alternative options to traverse to, from and around the urban core. These modes include walking, biking, CincyRedBike, buses, streetcar, uber, lyft, Gest, and Zipcar. In the near future, we’ll likely see Bird scooters and Lime bikes introduced. In the long-term, improved transit and autonomous vehicles will reduce the need to own and store a vehicle. Every one of these trips is one less parking space needed per resident, worker or visitor.
It would be wise for the City to anticipate criticisms from residents of the urban core. Some of whom recently voiced concerns regarding the increasing struggle to find on-street parking spaces. This is a struggle that is common in many dense, historic urban neighborhoods across the country where the expectation is that it is very rare to snag a parking space directly in front of a persons residence or business. However, it is important to consider this in light of a broader parking strategy, one that would balance resident, business and development demands.
There are a few additional strategies for city policymakers can consider in conjunction with approving the Parking Overlay District to remove parking requirements. Most of these are adapted from Dr. Shoup’s recommendations:
1.) Continue to pursue the implementation of the on-street residential parking permit program.
2.) Add on-street 10-30 minute convenience parking at some spaces around Findlay Market.
3.) Consider opportunities for future public underground parking facilities to serve Findlay Market and the rest of Over-the-Rhine north of Liberty Street.
4.) Enable the demand-responsive capabilities for on-street parking meters. This strategy will encourage more meter usage and could be a potential revenue add for the city’s parking meter program.
As part of a broader plan, it makes sense to remove the parking space requirements in the urban core. To quote Shoup, “If Cincinnati uses fair market prices to manage on-street parking – the lowest prices that will leave one or two open spaces on every block at every time of the day – it won’t have to require off-street parking spaces for every land use. If the government regulated any other aspect of our lives as precisely as it regulates the number of off-street parking spaces everywhere, everyone would join the Tea Party.”
Removing parking minimums is a productive first step in the city’s comprehensive strategy to balance the demands of residents, workers, visitors who help make our urban core a vibrant and attractive place. Supporting this policy is a step in support of enhancing housing affordability, historic preservation, environmental sustainability and livability in our urban core.
















 The walking tour is inspired by
The walking tour is inspired by