The City of Cincinnati passed yet another structurally imbalanced budget late last week. At the meeting Vice Mayor Roxanne Qualls (C) and other council members admitted that the approved budget once again relied on a one-time fix to get the city through another budget cycle without significant layoffs and major funding cuts.
The City of Cincinnati passed yet another structurally imbalanced budget late last week. At the meeting Vice Mayor Roxanne Qualls (C) and other council members admitted that the approved budget once again relied on a one-time fix to get the city through another budget cycle without significant layoffs and major funding cuts.
Despite having its hands tied in coming up with creative ways to find revenues, Cincinnati is not alone in dealing with this dilemma. Hundreds of cities across the nation are struggling with budget deficits with some much larger than ours.
Smart Growth America recently completed a national report, titled Building Better Budgets, with findings that could help many municipalities find long-term solutions to their budget crisis. The report makes three main arguments that smart growth development, described as compact, walkable and mixed-use overall save municipalities on upfront infrastructure costs, service costs and serve to increase the city’s tax base better than suburban style developments.
After reviewing a diverse collection of cities across America, such as Raleigh, NC, Nashville, TN and Champagne, IL, the study found that smart growth development costs an average of 38% less for upfront infrastructure, saves municipalities an average of 10% on ongoing delivery of services, and generates approximately 10 times more tax revenue per acre when compared to conventional suburban development.
“These figures are conservative, and many communities could save even more,” authors of the report stated. “Smart growth development’s potential for lower costs and higher revenues means that many municipalities can operate smart growth development at a surplus rather than a deficit.”
How local projects stack up
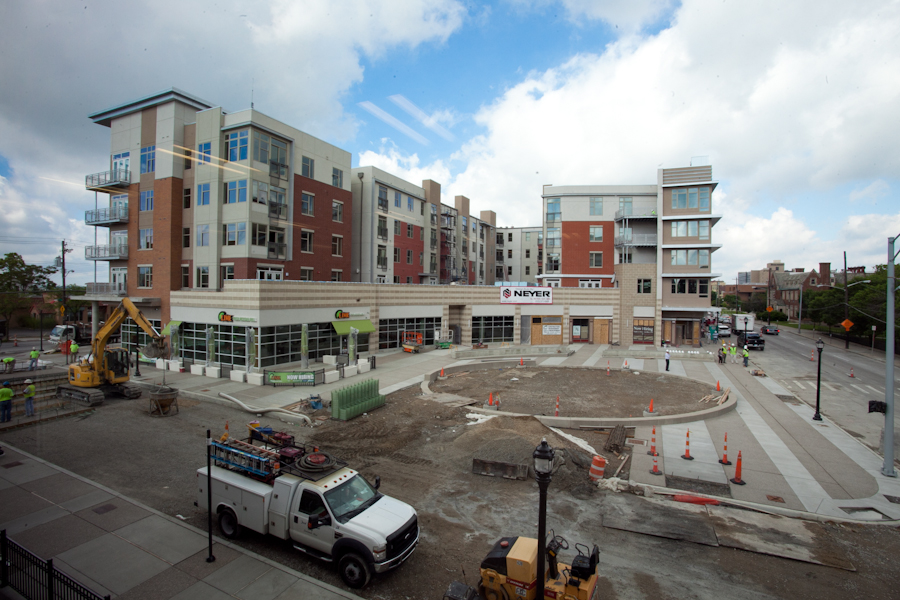
Several projects on the horizon are poised to add to the tax base in Cincinnati’s urban core. Phase two of The Banks, dunhumbyUSA Centre, the 580 Building apartment conversion, hotels at the Bartlett Building and Enquirer Building, and proposed apartment buildings above Fountain Place and the parking garage at Seventh and Sycamore all offer the upfront infrastructure cost savings and long-term revenue advantages discussed in Smart Growth America’s report.
The redevelopment of the Pogue’s Garage into a 30-story apartment tower with a grocery store, and an 11-store Holiday Inn at Broadway and Eighth Street are two other projects that offer similar benefits, but are currently on hold due to the ongoing legal dispute surrounding the City of Cincinnati’s Parking Modernization & Lease Plan. Additionally, a slew of projects in Over-the-Rhine, Walnut Hills and Northside also appear poised to help stabilize the city’s finances thanks to their smart growth advantages.

Not all is well, however, as many recent real estate investments throughout the city have taken the conventional suburban development approach. The Incline District in East Price Hill, Villages of Day Break in Bond Hill, Oakley Station in Oakley, MetroWest in Lower Price Hill, and developments along Red Bank Road in Madisonville all seem to be missing the bigger picture about the financial advantages of smart growth.
In addition to the actual footprint of the development, the report discusses the importance of a project’s site location.
“The per-acre measurement of tax revenue is extremely important because land is a precious commodity for every jurisdiction,” the report concluded. “It is true that in some cases the total dollar amount of tax revenue in conventional suburban settings can be very large, but those conventional suburban developments consume large amounts of land. Many cities in the United States have a constrained land supply and must husband their land resources carefully in order to protect their solvency.”
While many of the real estate investments throughout Cincinnati are being done in a smart manner, others seem to be squandering valuable urban land with suburban-style developments. The City of Cincinnati, and other cities around the region, might be able to make a long and sustained positive impact on their budgets by refusing to go forward with projects that offer an easy, short-term score, and instead demanding more sustainable development practices in their community.