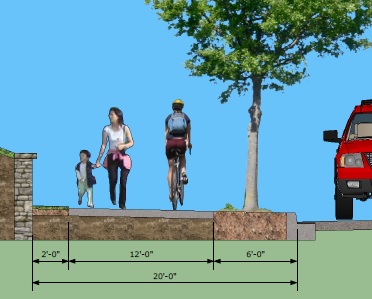
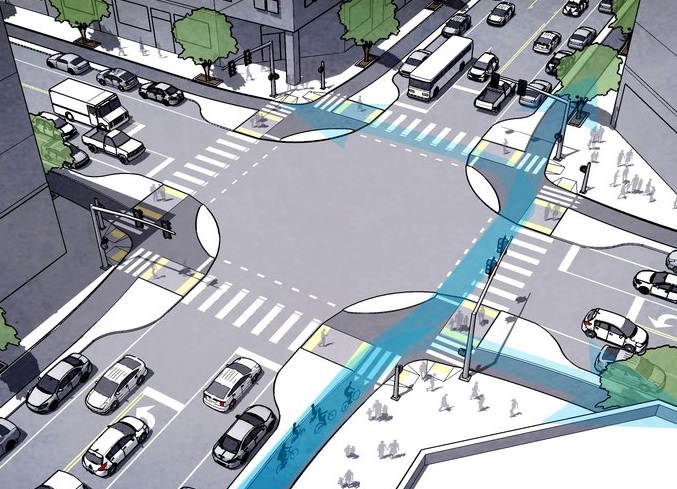
City and community leaders are taking a fresh look at some of Over-the-Rhine’s streets and intersections to see if they might be able to better function if managed differently.
In the 1940’s many downtown streets were converted from two-way to one-way traffic in order to stream automobile traffic through the city center. With the completion of Interstate 75 in the late 1950’s and Interstate 71 in the late 1960’s, some of these streets became important feeders into the highway system.
Additionally, many north-south streets, such as Main, Walnut and Vine, remained one-way to help move traffic throughout the new auto-oriented street system.
It eventually became clear, however, that one-way streets were not adding much benefit beyond moving vehicles slightly faster on their way to and from the interstate highways.
As a result, the City of Cincinnati spent around $400,000 in 1999 to convert Vine Street back to two-way travel from Central Parkway to McMicken Avenue. A subsequent study in 2004 found that traffic along Vine Street became slightly more congested, but also reduced the speed of motorists traveling through the historic neighborhood.
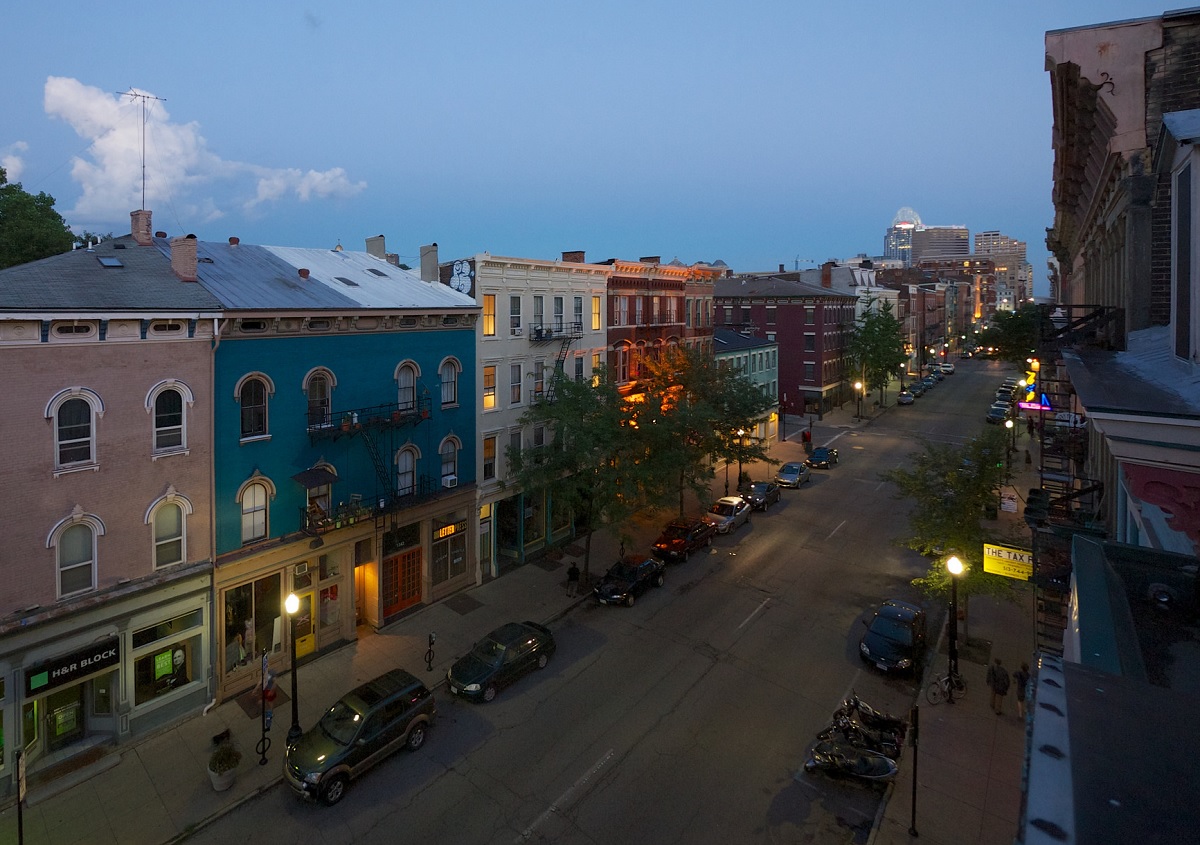
Since its conversion, Vine Street has also blossomed with dozens of new businesses, which can, in part, be attributed to slower traffic and improved access and visibility. As a result, there have been several other examples of this type of conversion throughout Over-the-Rhine, including sections of Thirteenth and Fourteenth Streets.
Two-way street conversions are typically credited with improving safety for pedestrians and cyclists, while also helping local businesses along the street by making it easier for drivers to navigate city streets. In addition to that, a civil engineer from Penn State University even found that the conversion of one-way streets can even improve traffic flow.
“Two-way networks can serve more trips per unit time than one-way networks when average trip lengths are short,” Dr. Vikash Gayah wrote in his essay. “This study also found that two-way networks in which left-turn movements were banned at intersection could always serve trips at a higher rate than one-way networks could, even long trips.”
Gayah’s conclusion was that the trip-serving capacity of a street network can actually be improved when converted to two-way operations, and when left turns are banned.
“This framework can be used by planners and engineers to determine how much a network’s capacity changes after a conversion, and also to unveil superior conversion options,” Gayah noted.
In Cincinnati, initiating such conversions can come in the form of streetscaping projects or through formal requests made by neighborhood leaders. From there, City engineers will determine the feasibility of suggested conversions. In some cases, like E. Twelfth, E. Thirteenth, Fourteenth Streets, City engineers have said that the streets are too narrow to be converted and remain one-way to allow for on-street parking.
The Over-the-Rhine Community Council recently submitted a request to the City to convert Main Street back to two-way traffic.
“At most times of the day Main Street has relatively light traffic and motorists speed down the street in order to make every green light,” Seth Maney, head of Main Street OTR, explained to UrbanCincy. “It can seem more like a drag strip than a pedestrian-oriented business district.”
The specific request from Over-the-Rhine activists is to convert both Main Street and Walnut Street. However, transportation officials say that the routing of the first phase of the Cincinnati Streetcar will prohibit such a conversion south of Twelfth Street.
“The streetcar route is something we have to consider if there was a desire to convert the north-south streets to two way traffic.” said Michael Moore, Director of Cincinnati’s Department of Transportation & Engineering (DOTE). “The conversion from Twelfth to Liberty Street, however, would be relatively simple.”
In addition to Twelfth Street, the streetcar’s routing along Elm and Race would also seem to make it improbable that either of those streets could be converted to two-way traffic.