CNU’s 2018 Transportation Summit was September 16-17 in New Orleans. The purpose of the summit was to bring together people focused on the revitalization of urban neighborhoods disrupted by freeways. In attendance were people from Massachusetts, California, Colorado, Texas, Wisconsin, Washington DC, and two members from CNU Midwest, Chris Meyer and Brian Boland. There were many takeaways from the summit but three lessons seem applicable to Greater Cincinnati.
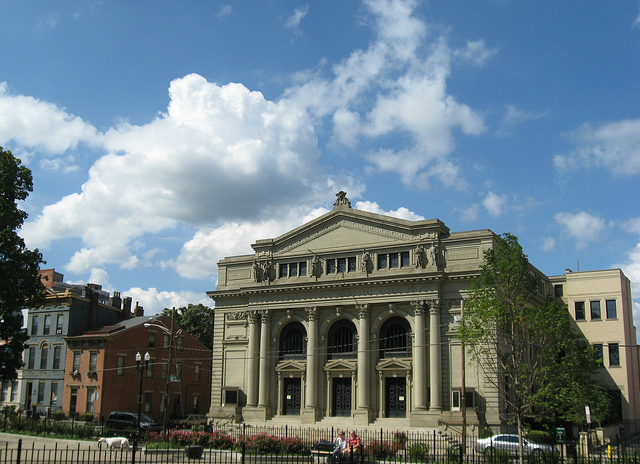
The first is that freeways and urban fabric are incompatible. Urban fabric in Greater Cincinnati typically consists of fine-grained parcels, 2-5 story buildings, and a dense street with grid pedestrian-scale streetscapes. Urban fabric is fundamentally sized for people. The 19th century blessed present-day Greater Cincinnati with an abundance of high-quality urban fabric. A minor takeaway from the transportation summit was that other cities would be jealous if they knew what we have.
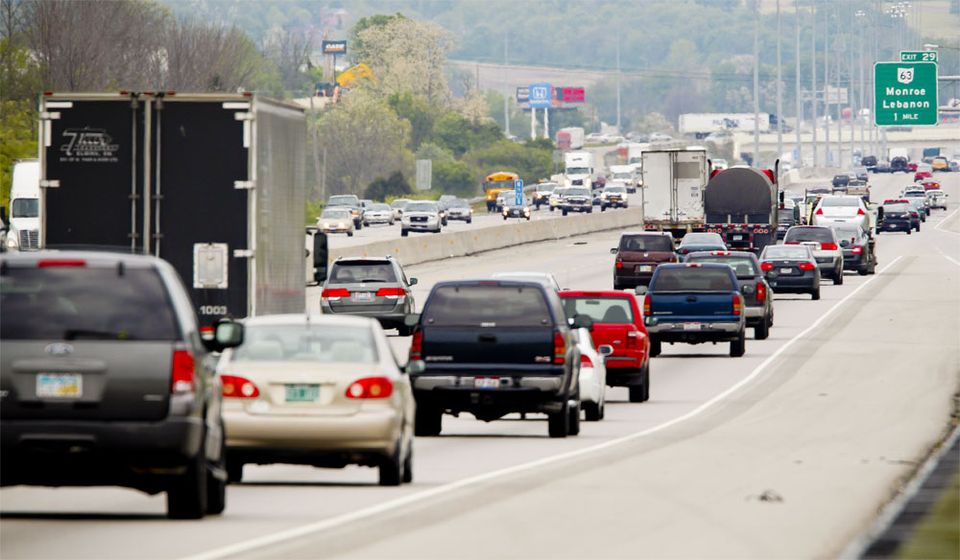
Freeways are scaled for cars and trucks. They are always interruptions in the urban fabric. They break up the street grid wherever they pass through it and form barriers to people passing. The urban fabric for blocks around a freeway is degraded not only by the dirt, noise, smell, and ugliness but also by the profusion of vehicles they concentrate and deliver into the urban fabric. This is true for greater Cincinnati along the I-75, I-71, and I-471 corridors.
Freeways are a necessary part of the urban economy but they are incompatible with the urban fabric. It was a mistake to run them through central cities. Dwight Eisenhower, the father of the interstate system, certainly thought so.
Multiple people at the summit noted that urban freeways are “monuments to racism.” That’s obviously the case in New Orleans. In Cincinnati, the West End neighborhood is physically gone but the Kenyan Barr photo exhibit, currently showing at the University of Cincinnati, illustrates the neighborhood destroyed by I-75. Ninety-seven percent of the residents were black.
A second lesson from the transportation summit is that urban fabric is valuable. Anyone familiar with CNU understands that. What was new is that urban fabric can be more valuable than the freeways running through it. Implicitly or explicitly, a big part of the argument to remove freeways, be it Denver, Oakland, or Austin, is to free up land for profitable new development.
The same principle applies to Cincinnati. The value of land with urban development on it is greater than the same amount of land with auto-centric development on it. The blocks around freeways are almost always taken up with auto-centric development because of how freeway ramps concentrate vehicles in a geographic space. Cincinnati would reap greater economic, tax, and social benefits if the space around Interstate-75 followed urban development patterns rather than auto-centric development patterns.
The third lesson is that the future of urban development doesn’t have to look like the past. When the first Congress for New Urbanism met in 1991, most new development was going to suburbs and central cities were still losing money and population. That has changed. People are moving back to places where they can live, work, and play, without a car. It’s happening in Cincinnati too.
Recognizing the value of urban fabric and the cost of freeways in the urban fabric allows people to recalculate the costs/benefits of future transportation projects. Two high-profile Cincinnati transportation projects include the Cincinnati Bell Connector streetcar and the Brent Spence Bridge expansion.
One argument against the streetcar is that it is not “profitable,” so it should be shut down. However, streetcars are compatible with the urban fabric. Most buildings and parcels on the streetcar route have been improved. Streetlife – outdoor dining, social interaction, economic activity – along the streetcar route is as vital as it’s been for decades. The streetcar is a fellow dancer in the sidewalk ballet. It improves the value of adjacent urban fabric, in opposition to freeways that destroy value. A better cost/benefit analysis of the streetcar would include the increased tax value derived from adjacent improved parcels.
The inverse argument occurs with the Brent Spence Bridge project. The primary cost/benefit evaluation looks at congestion. The potential value of restored urban fabric has never been a part of the bridge’s cost/benefit analysis. When they factored the value of urban fabric into the Fort Washington way redesign, they decided to sink the freeway below grade so it could be capped in the future. It’s easy to envision a redesigned bridge project that includes land for new urban fabric, much as the Fort Washington Way project did.
The 2018 CNU transportation summit brought together thought leaders, local activists, transportation professionals, and city designers. A repeated statement at the 2018 summit was that multi-million dollar infrastructure projects should improve the value of places where they are constructed. In Greater Cincinnati, it seems like the value of place is often not considered in the cost-benefit analysis of large transportation projects.
In the past, it was possible to argue that urban fabric had no value, or that its value was equal to auto-centric development. Those arguments can no longer be made in good faith. If Cincinnati is going to capitalize on the wealth of its urban fabric, the value of that fabric must be included when evaluating future transportation projects. If it’s done so accurately, we should be all the wealthier.
This is a guest article by Chris Meyer reporting on the 2018 CNU Transportation Summit. CNU and CNU Midwest are content partners with UrbanCincy. Chris is an Architect at Hub + Weber, PLC
If you would like to have your thoughts and opinions published on UrbanCincy, simply contact us at editors@urbancincy.com.















 The candidates for Cincinnati City Council and Mayor have faced off in a number of debates and forums over the past several months. However, one forum being held tomorrow will be of particular interest to readers of UrbanCincy.
The candidates for Cincinnati City Council and Mayor have faced off in a number of debates and forums over the past several months. However, one forum being held tomorrow will be of particular interest to readers of UrbanCincy.