In the United States, more than 45 million working-age adults – over 20% – speak a language other than English in their homes.
According to a report released by the Brookings Institute, approximately 19.2 million (almost 10%) of this sub-population are considered “limited English proficient” (LEP). More than 70% of these LEPs participate in the work force, and the Brookings Institute found that they make considerably less (anywhere from 17-135%) than their English-proficient counterparts. These individuals, researchers found, are also more likely to suffer from unemployment and poverty.
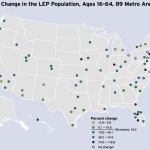
While most LEP individuals live in the nation’s large metropolitan areas, like Cincinnati, their numbers are rapidly growing in smaller urbanized regions, like Dayton and Lexington.
In the Cincinnati metropolitan region, the number of LEP adults exceeds 35,000 and has grown 55.1% since 2000. This places the region in the top 25 of the 89 largest metropolitan areas in the nation; however, LEP individuals only make up 2.5% of the metropolitan region’s total workforce. This places Cincinnati 88th out of the 89 largest regions in America.
There has been a growing interest in this topic recently, with some organizations going as far to organize workshops to help non-native English speakers with business start-up and management training.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the report found that the most commonly spoken language by LEP individuals is Spanish. Across the nation, that percentage is 66.3%, but represents just 41.9% of the LEP population locally.
The Cincinnati region does, however, have a relatively high percentage of Asian and Pacific Island language LEP workers (35.2%), with Chinese, Vietnamese, and Japanese following Spanish as the top languages spoken. French speakers come in next at 3.9%.
It should be emphasized that while Germans represent the region’s predominant historical migrant community, the German language did not rank amongst the top five languages spoken within Cincinnati’s LEP community. This, however, may be the result of Germans immigrating to the region several generations ago. It also speaks to the complexity of the issue of immigration and the need for a comprehensive study of the matter.
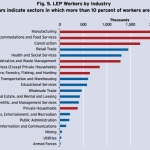
Following national trends, the Brookings Institute found that LEP workers in Cincinnati are most likely to work in industries like manufacturing, accommodation and food service. Cincinnati’s LEP workers, however, were found to be slightly more educated than the national average, with a smaller percentage of individuals with less than a high school education and a larger percentage of individuals with an education level of at least some college or a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Those positive numbers seem to translate into better economic performance for the region, with more than 76% of Cincinnati’s LEP workers active in the regional workforce – a rate that is slightly better than the national average.
With demographers predicting that almost all growth in the U.S. labor force will come from immigrants and their children over the next half-century, these statistics have a large impact on the overall well-being of the American economy.
EDITORIAL NOTE: Listen to our podcast with Alfonso Cornejo, President of the Cincinnati Hispanic Chamber, and Kristin Hoffman, an Immigration/Administration Lawyer with Hammond Law Group, to learn more about the region’s efforts and needs to become more welcoming to immigrants and foreign language speakers.