When a brother and sister are fighting over the same toy, a parent quickly steps in and teaches the children to take turns and share.
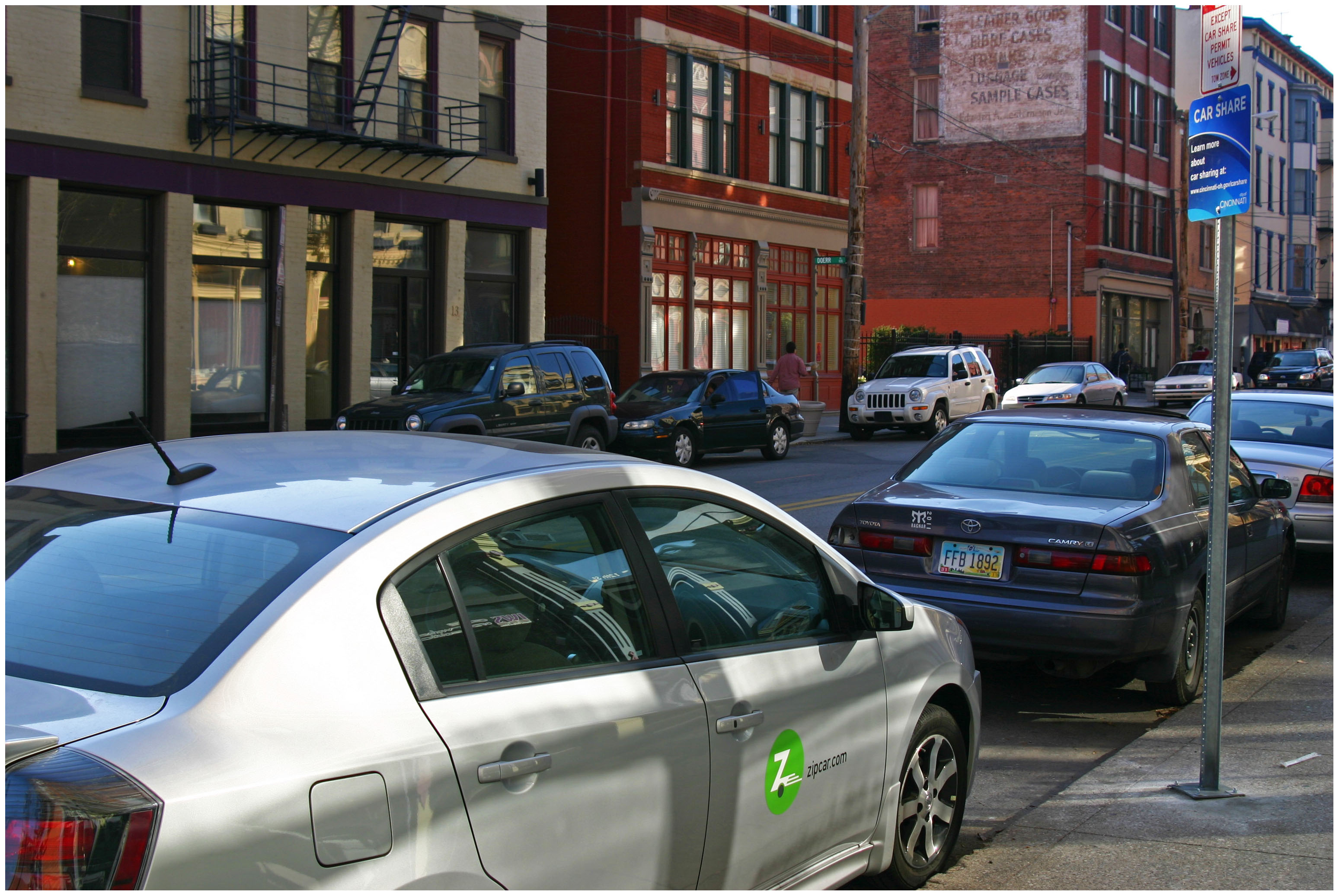
Now that Over-the-Rhine parking is at a premium, and the residential permit plan has been vetoed, the residents of OTR are going to have to find a way to share parking, or risk losing more of the historic neighborhood to parking lots and garages. Sharing also presents an opportunity when it comes to modernizing the City of Cincinnati’s fleet of 2,149 vehicles.
Mayor John Cranley (D) received unanimous support for this year’s budget, which includes $110 million to make much-needed upgrades to the City’s fleet and roadways over the next six years. While some vehicles, like those for police and fire, cannot be shared, others certainly can; and by implementing a program like Zipcar’s FastFleet program, Cincinnati would benefit from significant savings and operating efficiencies.
In 2012, an internal audit of the Fleet Services Division found that fleet management has been “unwieldy” and mentioned that a knowledgeable and empowered staff is needed to properly manage the system. This has proven difficult over the past decade due to a severe cut in funding for the department in 2003.
“Almost the entire management team left the department near the end of 2007 and was not replaced,” the internal audit noted. “While the staff operates to the best of their abilities, they are undermanned without the resources to correct the inertia of the department.”
The Fleet Services Division operates under the Public Services Department, and controls and maintains 2,149 motorized vehicles for various departments at City Hall. These departments pay $63 an hour for maintenance and repair of the vehicles and are allocated a portion of the capital budget based on their proportion of need with regards to their percentage of obsolete fleet.
In 2011 Fleet Services was allocated $4,301,900 in capital dollars and $5,240,600 was allocated for 2012. These numbers are expected to rise as soon as the approved budget is published on July 1, but more money for new vehicles is only part of the solution. The 2012 audit also recommended reducing the size of the fleet, evaluating underutilized equipment, and examining the cost of leasing sedans and light trucks.
With services like FastFleet, City Hall could optimize its fleet without degrading operations, thus lowering maintenance and administrative costs.
FastFleet works by tracking vehicle usage by employees through GPS monitoring systems. This enables the service to produce real-time data, with recommendations on synergy and optimization. Once this data is analyzed, car assignments can be reorganized to allow for sharing of each vehicle by city employees, ultimately allowing for more efficient usage of vehicles.
In Washington D.C., city officials there were able to benefit from $6 million in savings over a five-year period by eliminating more than 200 administrative vehicles from their fleet. While Cincinnati’s fleet is smaller than the nation’s capital, proportional savings are safe to be assumed.
With City Hall poised to invest millions into its fleet operations, now is the perfect time to look into a solution such as this that could potentially reduce the City’s fleet, while also improving its performance.
A program could even be put in place to allow for public use of the vehicles, akin to the city’s existing Zipcar system, when city employees are not in need of the fleet. The revenue collected from these services could then be used to offset the public’s cost of maintaining the city’s fleet, while also expanding car-sharing services to other neighborhoods outside of the city center.
As it stands now, the City of Cincinnati does not even know what the optimal size is for its vehicle fleet. Tracking the performance of the fleet and analyzing the data will help bring clarity to the matter, and allow for the fleet to perform more efficiently.
Implementing a vehicle sharing program for Cincinnati’s municipal fleet would help save additional taxpayer dollars, improve operations and bolster car-sharing throughout the city.
EDITORIAL NOTE: Chad Schaser contributed to this article.