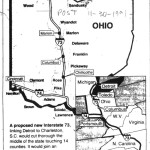
An event making the rounds on social media hosted by the Ohio Department of Transportation (ODOT) provides an opportunity for citizens to tell Governor John Kasich’s (R) administration about public transportation improvements they’d like to see in their city. The public meeting to discuss statewide transit needs is hosted on Friday, October 31 from 10am to 12pm at the Warren County OhioMeansJobs Center in Lebanon.
While the gathering has good intention, it fails to meet the basic criteria of planning a public involvement meeting:
- Never host a public meeting on a holiday.
- Never host a public meeting on a Friday or weekend.
- The location of a public meeting should be accessible to all members of the community and able to attract a diverse group of citizens.
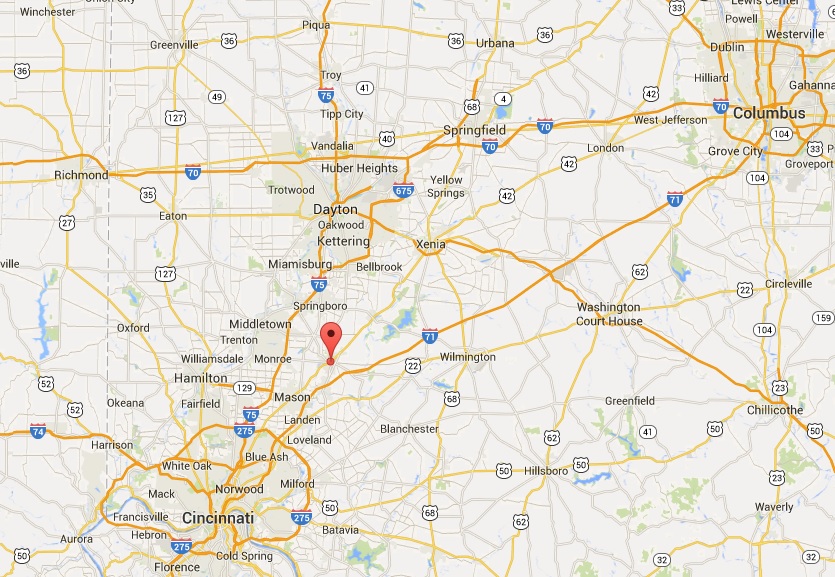
By car, Lebanon is roughly a one hour drive north of Cincinnati, and a 30-minute drive south from Dayton. It’s also the city where the regional ODOT office is located; understandably why the administration would opt to hold a public involvement meeting here. What went unconsidered are the needs of people that the public meeting is focused on: citizens reliant on public transportation.
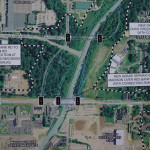
The closest Metro bus stop to Lebanon is 8.3 miles away, near Kings Island in Mason. Let’s say we’re feeling ambitious and attempt to take the bus, then bicycle the remaining journey to Lebanon. It would take 48 minutes to cycle to the meeting in addition to the 1 hour, 11 minute ride on the bus. Cincinnati Metro, the region’s bus system, only offers select service to the northern suburbs. In order to arrive on time for the 10am meeting, a person dependent on transit would have to catch the 71x at 7:45am, arrive in Mason at 8:52am, then continue to the meeting on bicycle.
Getting back home is another story. The public involvement meeting adjourns at 12pm, but the bus route that services Mason is a job connection bus, meaning it only runs traditional hours when people are going to and from work. After another 48 minutes of cycling back to the bus stop, the inbound 71x picks up shortly after 3pm and returns to Cincinnati at 4:40pm.
In summary, if a citizen dependent on bus transportation wishes to give ODOT their input, they would spend 7 hours commuting to the two hour meeting, and need to able-bodied to ride a bicycle for eight miles. What about senior citizens and people with disabilities? Who can afford to take an entire day off work to attend a meeting? As a transit rider who has a car, driving an hour each way to attend the meeting –in the middle of the work day– for me, is inconvenient and unfeasible.
The poor choice of trying to combine Cincinnati and Dayton into one meeting was an unfortunate oversight in event planning. Instead, meetings should be hosted in the downtown of each city, just like they have been in Columbus and Cleveland which are also participating in the ODOT series.
Since 2011, Governor Kasich has cut $4 million from the state’s public transit budget, leaving Ohio with one of the lowest funded transit systems in the country. If there’s a genuine interest in hearing how those cuts affect the people that rely on public transportation the most, the administration needs to schedule a second meeting in Cincinnati near Government Square where those people can actually get to.
Of course, this isn’t the first time area transit users have been ignored when it comes to public meeting locations. Earlier this year, Ohio Secretary of State Jon Husted (R) upheld a decision to relocate Hamilton County’s Board of Elections office to a location that would take up to four hours to access by transit.