The growth of intercity passenger rail and bus continues. According to newly released data, the National Railroad Passenger Corporation (Amtrak) recorded a record breaking year in terms of both ridership and revenue.
The data is for FY13, and showed that the oft-criticized passenger rail agency carried 31.6 million passengers and collected $2.1 billion in ticket revenue. Amtrak officials say that the ridership figure represented a 1% increase while revenue was 4.2% higher than the previous year.
In addition to the ridership and revenue growth, Amtrak also broke several records over the past year including total ridership in one month (March; July), ridership records on 20 of the agency’s 45 routes and the number of passengers using state-supported routes (15.4 million) in a single year.
When compared with other modes of transportation, Amtrak now has more than double the ridership of Greyhound, and if it were a commercial airline it would be the fifth largest domestic carrier.

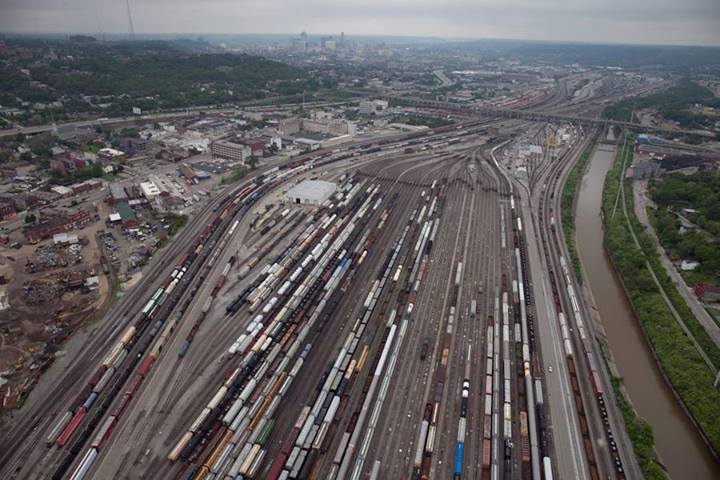
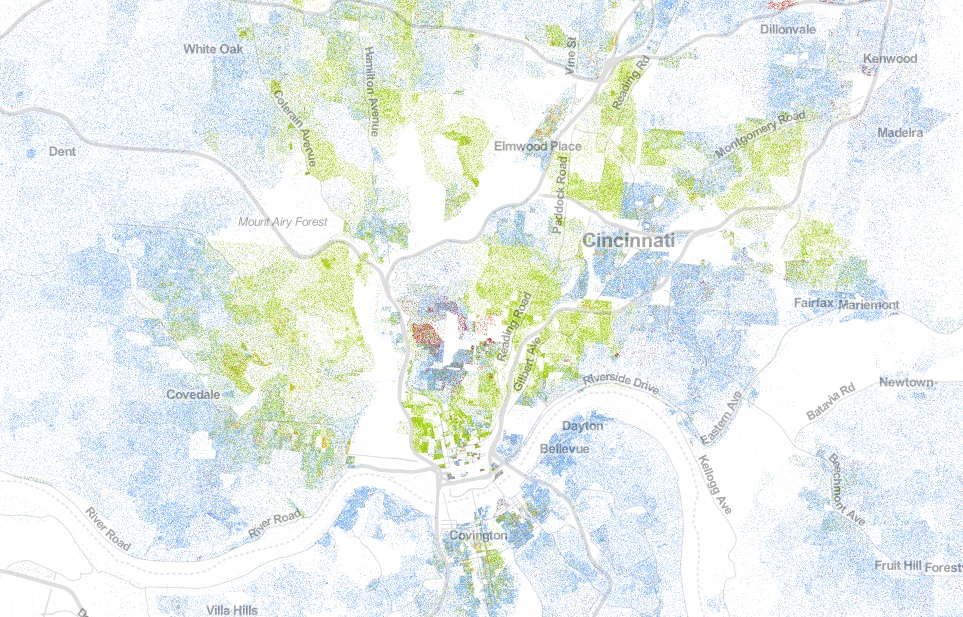
Cincinnati has largely been on the outside looking in when it comes to Amtrak ridership growth, but unclogging the Midwest’s second busiest railyard will need to come first. Photograph by Jake Mecklenborg for UrbanCincy.
“In ten of the last 11years, we have marked new ridership records, and since ridership has risen by 50% since FY2000,” Amtrak’s President and CEO, Joe Boardman, told employees through an internal memo. “This great accomplishment is not solely ours, but was made possible through strong, collaborative relationships with our state partners and the federal government.”
Boardman went on to say that through these relationships, Amtrak will pursue the resources needed to rebuild and enhance passenger rail service throughout the country, and work toward building infrastructure to support high-speed rail.
As a result of these partnerships and ridership growth, Amtrak now recovers approximately 85% of its annual operating expenses from user fees.
“I believe that all of these records point to our success in creating and marketing a product desired by the traveling public,” Boardman explained. “In growing metropolitan areas, passenger rail is clearly a viable alternative to crowded roads and skies, while in many rural areas, Amtrak often is the only means of regularly scheduled, public intercity transportation.”
While Amtrak’s success has been felt nationwide, very little has been felt here at home in Ohio due to limited service in the nation’s seventh most populated state. The reason, passenger rail advocates say, is because of a lack of support from the State of Ohio.
“We are on the outside looking in. Ohio isn’t on the outside due to a lack of travel, as USDOT says travel on Ohio’s stretch of I-71 (Cleveland-Cincinnati) ranked 22nd in the country with nearly 5.5 billion vehicle-miles traveled in 2011,” noted Ken Prendergast, Executive Director, All Aboard Ohio. “In the Midwest, only I-94 through Michigan (Detroit-Chicago) saw more traffic in 2011.”
Prendergast went on to note that the stretch of I-94 through Michigan is currently being upgraded to 110mph service by the Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT), with some stretches operating at that speed already.
The situation in Ohio has been bad for a long time, but got significantly worse following the election of Governor John Kasich (R) in 2010. Almost immediately after taking office, Kasich gave away $400 million from the federal government that was intended to establish passenger rail along the 3C Corridor. The stretch between Cincinnati, Columbus and Cleveland is seen as the most densely populated corridor in North America without any passenger rail service.
Not all hope for Ohio, however, is lost. On National Train Day this past May, Cincinnati Mayor Mark Mallory (D) commended the work being done by Amtrak and called for enhanced service and operations out of Cincinnati’s Union Terminal.
“Passenger rail has to be part of a balanced multi-modal transportation system that I believe the federal government needs to play a huge role in in addition to states and local governments,” Mallory stated at Cincinnati’s National Train Day event on May 11. “Indiana has made a lot of progress as it relates to Amtrak…wouldn’t it be great to be able to jump on a train in Cincinnati, run to Indianapolis and then on to Chicago? I want Cincinnati to be a part of that line.”