President Barack Obama (D) was reelected on Tuesday, November 6. President Obama won approximately 51% of the popular vote, but won in convincing fashion with the Electoral College, earning 332 out of 578 total electoral votes.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, cities appeared to deliver the victory of a second term for President Obama this election season. According to Edison Research, President Obama earned approximately 69.4% of the vote in cities with more than 500,000 people, and 58.4% of the vote in cities with 50,000 to 500,000 people.
Furthermore, with the exception of Jacksonville and Salt Lake City’s home counties, President Obama won the plurality of votes in every major American city. This includes Cleveland, Columbus, Cincinnati, Toledo, Dayton, Akron and Youngstown in Ohio.

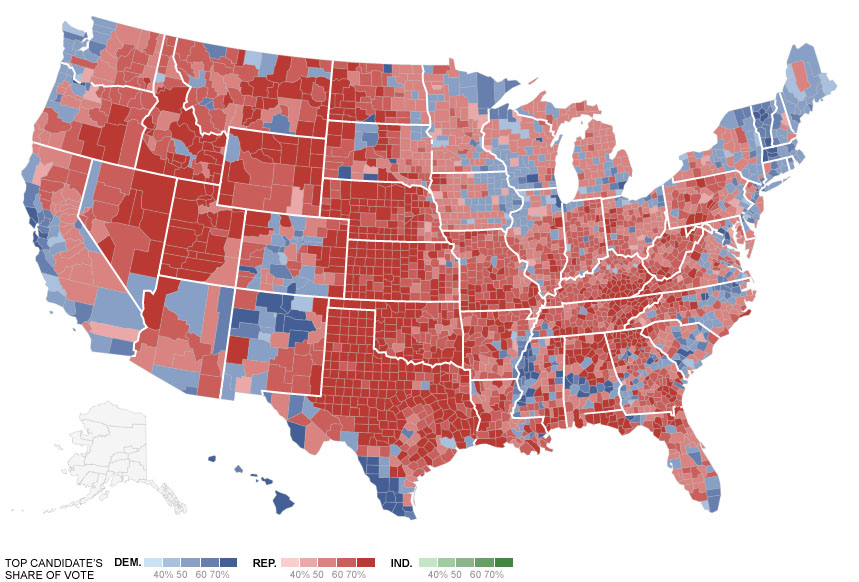
The President Obama won all but two counties with major cities, and swept the major demographics that are changing urban American. Map courtesy of The New York Times.
The browning of America
Cincinnati’s traditionally conservative Hamilton County has been trending more liberal over the past decade. Over that same time frame, American cities have seen a long foreseen demographic shift take root.
In 2012, the U.S. Census Bureau found that minority babies are now a majority of those born in the United States, and that 50,000 Hispanics reach voting age every month. Furthermore, 11% of all U.S. counties are now majority-minority, and half of the 40 largest metropolitan regions now have a while population below 60%.
The trends, when compared with the results of the 2012 election, are profound.
According to NEP Exit Poll conducted by Edison Research, President Obama earned the vote of 92.7% of black voters, 70.6% of Hispanic voters, 73.2% of Asian voters, and 57.7% of all other non-white voters. Mitt Romney, however, did earn the vote of approximately 58.7% of white voters.
Not only are these demographic groups growing in numbers, they are increasingly showing up to vote, with both black and Hispanic voters showing up in record numbers for the second consecutive presidential election.
The single, urban woman
Single women are another increasingly powerful force behind the resurgence of cities. There are an estimated 17 million women who live alone in America, and President Obama won that voting bloc by a whopping 39%.
Sociologist Eric Klinenberg attributes the foundation for this demographic shift to larger cultural changes in American society. In his book, Going Solo, he describes the rapid entry of women into the civilian workforce over the past 40 years, the delay of marriage for young people, and the “divorce revolution” that took place during the 1970s.
In short, young people, especially young women, are much different in contemporary America than those from 50 years ago.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the number of women in the workforce has grown from 14.8 million in 1967 to 43.2 million in 2009. And in 2009, it is estimated that approximately 30% of all women over the age of 25 have earned a bachelor’s degree or more.
Should these trends continue, the single urban woman may continue to become an even more powerful voting bloc.
With single women and minorities becoming an increasingly dominant portion of 21st century American cities, it may force the hands both major political parties to focus more of their energy on public policies that positively relate to urban voters.