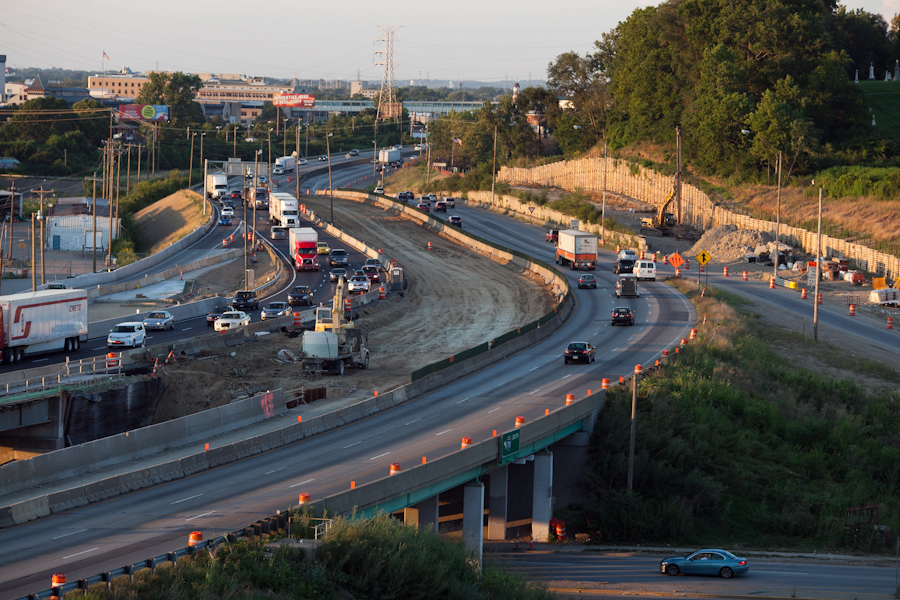
While Ohio’s gas taxes and population have remained flat over the past decade, the Ohio Department of Transportation has continued to add capacity to roadways across the state – in some cases even building entirely new roadways to add to the state’s existing infrastructure. This may all soon be ready to change in what is being called a “major” policy shift in Columbus.
According to employees at ODOT who were briefed at an internal meeting on the matter recently, the nation’s seventh-largest state is poised to announce in the coming months that the days of roadway expansion are over. Instead they say that ODOT will embrace a future focused on maintenance and preservation of its existing network of more than 43,000 miles of roads and 14,000 bridges.
While officials say the move is economically driven, it also comes at a time as activists around the country – including numerous cities throughout Ohio – are increasingly calling for governments to embrace a “fix-it-first” policy.
An increasing number of states have been adopting such policies, with Michigan being one of the first when it enacted its Preserve First program in 2003, and California being the largest when it joined the fray last year.
The forthcoming announcement from ODOT, however, goes a step further than that.
In addition to focusing funds on maintenance and preservation, ODOT officials also say that they will abandon their “worst first” approach to fixing existing roadways. In doing so they say that the new program, called the Transportation Asset Management Plan, can save the state an estimated $300 million over the next six years – money that can then be redirected to other preservation activities like cleaning, sweeping, sealing and micro-surfacing.
The idea here, similar to healthcare or household maintenance, is that it is often much more economical to make steady improvements rather than waiting to make repairs until the asset is too far gone.
“It’s finally sinking in that we cannot continue on this unsustainable pace of highway expansion,” said an ODOT employee who spoke to UrbanCincy on the conditions of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak publicly.
According to ODOT’s own internal estimates, current funds will not be enough to maintain Ohio’s existing system by 2019 – the time when the Ohio Turnpike bonds are gone. Thus, without a major new source of revenue like a gas tax increase, ODOT intends to completely get out of the highway expansion business, and shift all funds to maintenance and rehabilitation.
“Most projects will occur before a road becomes severely compromised, and will be based around maximizing the service life of a particular road,” the ODOT staffer continued. “Long story short, ODOT isn’t going to waste its money on patching up a road as a temporary fix that will simply deteriorate again quickly because of major structural problems.”
There is no clear idea as to whether highway expansion projects currently on the drawing board will be impacted by this, but it appears likely that they will unless they receive capital funding through TRAC prior to 2019.
Such news could be damning for projects like the recently proposed Eastern Bypass or what is left of the Eastern Corridor project. At the same time, it could be the positive jolt needed for projects like the Western Hills Viaduct, which is in desperate need of an estimated $280 million fix.