Cincinnati has a migration problem that is two-fold. First, it lags behind most major metropolitan regions in North America when it comes to attracting international migrants. Second, and perhaps more significantly, is that the region has a stagnant domestic population.
This is not because domestic migrants are any more or less important than international migrants. But rather, it is because stagnancy is a major problem for cities.
As many demographers and social scientists have pointed out, focusing public policy on retaining existing talent is a bad approach. In fact, large movements of people out of one region can be a very positive thing. That is, of course, if it is balanced out by a large influx of people into that same region. This is the case for North America’s largest cities, and is also evidenced at a larger scale in California.
But beyond that, older Midwestern cities with a large cluster of high-quality universities also seem to export more people than they import. That, in and of itself, is not the problem.
“This notion of the university as a “factory” gets very close to the truth,” Aaron Renn, owner of The Urbanophile, wrote in 2010. “A friend of mine noted that if we treated steel mills like universities, Indiana would be obsessing over “steel drain” and spending hundreds of millions of dollars on programs to try to keep steel from leaving the state.”
Renn went on to say that the notion of doing such a thing would be ludicrous, and that it is important to understand the details of what is really going on when it comes to a region’s migration patterns.
“Migration does matter. Any city that thinks it can be blasé about this is fooling themselves,” wrote Renn in a separate piece. “On the other hand, surface numbers only tell us so much. We need to understand the dynamics going on underneath the hood.”
By most comparative measure, Cincinnati actually does very well compared to many places at retaining its population. The problem is that it does very poorly at bringing in new people from outside the region.
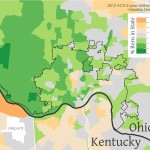
Based on five-year estimates from the American Community Survey, this stagnation can be clearly seen.
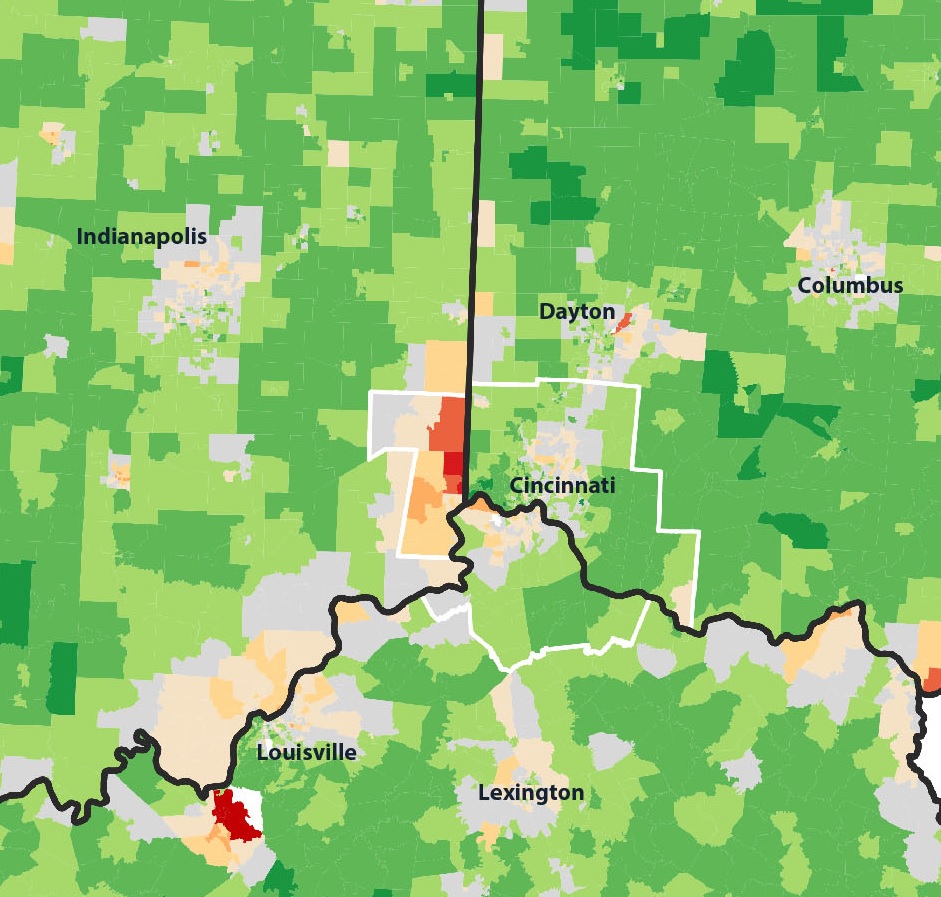
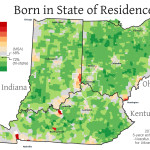
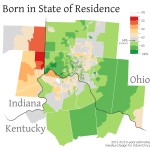
Perhaps not surprisingly, the areas of the Cincinnati Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) which have the highest percentage of people living there that were born in another state are near state borders. Since the Cincinnati MSA stretches across three states, you can see that movement of Ohio residents to southeastern Indiana and northern Kentucky has boosted numbers in those locales.
On average, approximately 68% of the 2.2 million person Cincinnati region was born in the state where they currently reside. Meanwhile, Uptown and Cincinnati’s northeast suburbs appear to be the only parts of the region that are actually attracting newcomers to the region.
Another key finding here is the utter lack of movement of people into or out of Cincinnati’s western suburbs, which have a native born population between 80-100%. This number is roughly comparable to most rural areas in Ohio, Kentucky and Indiana.
The Cincinnati region, however, is not alone when it comes to a stagnant population.
While Columbus was seen as a leader amongst big cities in terms of its domestic migration rate, it appears that Columbus is merely attracting new residents to its region from elsewhere in Ohio. Almost the entire Columbus MSA has a native born population between 60-80%.
The numbers are even worse for the Cleveland MSA, which, on average, has a percentage of native born population higher than the average for Ohio, Kentucky and Indiana. This is in spite of the Cleveland MSA attracting more international migrants than any other in the three-state region.
Even though Cincinnati continues to post modest annual population growth, it continues to be on the outside looking in when it comes to North America’s most economically successful cities. If Cincinnati wants to just focus on attracting existing Americans to the region, then it should look to Houston, Dallas or Atlanta, which are all hubs for domestic migration.
This scenario, however, seems unlikely since each of those regions is positioned uniquely in terms of their economy or their geographic location. So, if Cincinnati is to really ramp up its population growth, it better look at what other metropolitan regions are doing to make themselves more attractive to international migrants.
Perhaps Mayor John Cranley’s new, yet-to-be-unveiled initiative can help with this. But does he or his administration actually know what is going on underneath the hood?