Thanks to a $450,000 donation from Duke Energy, the Cincinnati Park Board will be able to move forward more quickly with the development of what was previously called the Main Street Garden at the Smale Riverfront Park.
The area is located immediately south of Great American Ball Park, and is now called the Duke Energy Garden. The narrow piece of park space is expected to be completed by spring 2013, and will connect the Smale Riverfront Park with additional riverfront parkland to the east (Sawyer Point, Bicentennial Commons, Theordore M. Berry International Friendship Park).

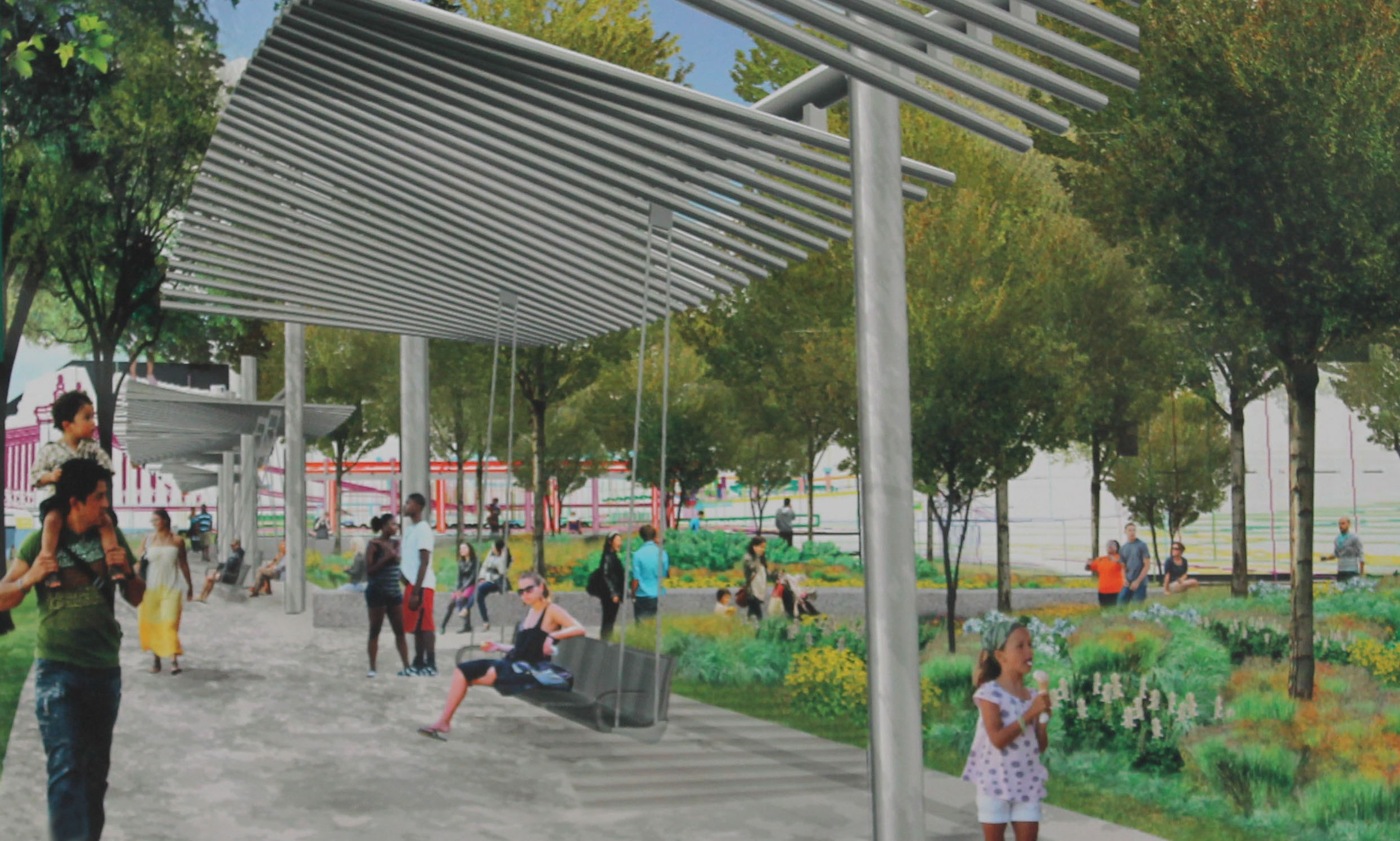
The Duke Energy Garden will include 12 “family-sized” porch swings, walking paths, and will help connect the Smale Riverfront Park with additional riverfront parks to the east. Rendering provided.
According to Cincinnati Park Board officials, this connection will be further established with the completion of the Ohio River Trail to Paddlewheel Park in fall 2013.
“The Cincinnati riverfront is more than just an entryway into our community,” Julie Janson, President of Duke Energy Ohio/Kentucky, stated at a Monday morning press conference. “It serves as the front porch to Ohio. That’s why Duke Energy, through our foundation, is happy to be able to support the creation of the Duke Energy Garden in the new Smale Riverfront Park.”
According to park officials, the Duke Energy Garden will include 87 trees, thousands of smaller plantings, walking paths, a 150-foot granite seat wall, and 12 “family-sized” porch swings.
The porch swings will be suspended from “undulating” pergolas that will also offer park-users a bit of shade and protection from the elements while enjoying the swings, which have long been anticipated at the park due to their popularity elsewhere throughout the country.

Three additional phases of work are planned to follow the completion of the Duke Energy Garden at Smale Riverfront Park. Image provided.
“Duke Energy’s commitment to the vitality of this region has been demonstrated again and again by the company’s substantial investments in economic development, education, environmental and energy efficiency efforts throughout the region,” said Willie F. Carden, Jr., Director of Cincinnati Parks. “The establishment of the Duke Energy Garden in Smale Riverfront Park is another such gift that will provide a stunning new public greenspace in Greater Cincinnati’s grand new front yard.”
The majority of phase one work at the Smale Riverfront Park was completed in May 2012, but several features of phase one have yet to be funded or built, in addition to future phases of park construction to the west. Some of those features include a transient boat dock, playgrounds, additional gardens and tree groves, a carousel, and more promenades and fountains connecting the central riverfront park with the Ohio River.
Three additional phases of construction work will take place following the completion of the Duke Energy Garden, and it is expected that once fully built out that Smale Riverfront Park will attract approximately 1.1 million visitors annually.