In February 2011 UrbanCincy challenged Cincinnati transit leaders to create a universal transport payment system that would rival the world’s very best. The challenge was made, in part, because we knew an overhaul of Metro’s 17-year-old fare collection system was imminent.
In February 2011 UrbanCincy challenged Cincinnati transit leaders to create a universal transport payment system that would rival the world’s very best. The challenge was made, in part, because we knew an overhaul of Metro’s 17-year-old fare collection system was imminent.
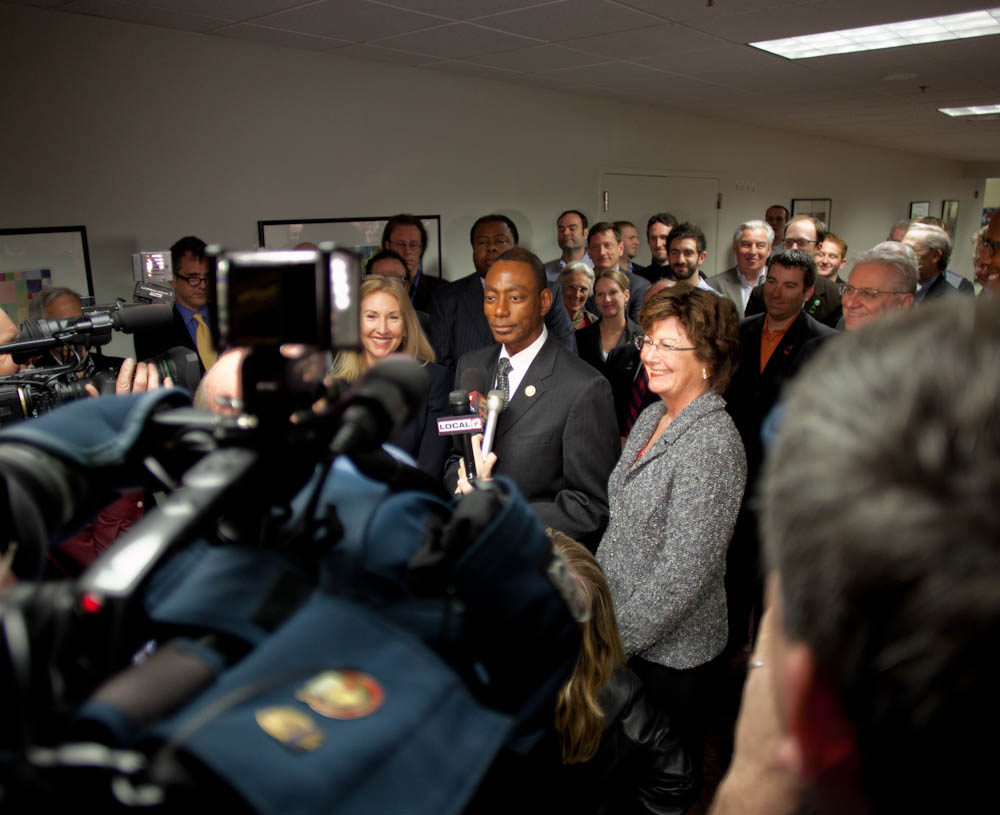
On Friday Metro officials announced those long-anticipated changes. By the end of 2011 Metro will install new fareboxes on their entire 333-bus fleet. The new fareboxes will utilize smartcards that can be loaded with monthly passes or set pay amounts ($10, $20 or $50). The use of smartcards will allow riders to simply tap-and-go, and it will allow transit planners to more accurately track ridership patterns system-wide. The new GFI Odyssey fareboxes will also automatically issue transfers upon payment.
“One of our goals is to make riding Metro easier and more convenient for our customers and potential customers,” Terry Garcia Crews, Metro CEO, said in a prepared statement Friday. “The new fareboxes will help Metro boost productivity by generating detailed ridership data that Metro needs to manage our service.”
Each year Metro collects approximately $23 million in fares, which accounts for roughly 27 percent of Metro’s total operating revenue. The new fareboxes are being purchased largely through a $3.6 million federal grant which is providing 80 percent of the total cost. The remaining $900,000, officials say, will come from local funding.
Officials say that future improvements may be made to the smartcards that could allow for more flexible spending accounts, but for now only set payment amounts will be accepted. While the system is an enormous improvement over Metro’s nearly two decade old system, it still falls short of UrbanCincy’s challenge.
As currently planned, the system does not integrate with the other regional transit agencies or with local businesses, and there is no mention of the smartcards compatibility with financial institutions. Furthermore, the new system does not integrate with other modes of transport like taxis or the University of Cincinnati’s bike share program, for example.
As the new GFI Odyssey farebox system is implemented over the next six months, regional leaders should meet to discuss how this $4.5 million investment should be leveraged to improve Cincinnati’s quality of life for tourists, businesses and residents. A truly integrated payment system, like London’s Oyster Card or Seoul’s T-Money Card, has the ability to change the game. Cincinnati should be so bold.