We take for granted that bridges, roads, highways, water treatment facilities and dams will function as expected and take us to where we need to go. But our nation’s aging infrastructure has long been in decline as money is diverted from maintenance to construction of new projects, many times for politicians eager for the photo op of a ribbon cutting event.
Recently, the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) released its latest report on the current state of the nation’s infrastructure. The last such report, issued in 2009, had given the country a rating of D. This year’s report showed the nation’s rating had improved to a D+ grade.
“Our country’s association of civil engineers continues to do the yeoman’s work of sounding the alarm on our country’s infrastructure — the roads, rails and waterways that we depend on to move our goods from place to place and get us where we need to go each day,” James Corless, Director of Transportation For America (T4A), stated in a prepared release.

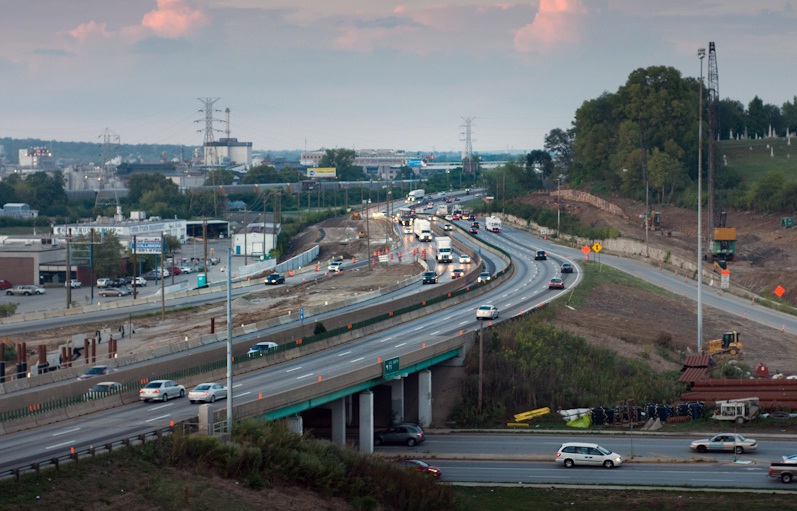
Work on the multi-billion dollar repair and widening of I-75 through Cincinnati proceeds, but the project still has yet to receive the full funding it needs to be completed. Photograph by Jake Mecklenborg for UrbanCincy.
As the nation sifts through a backlog of infrastructure replacement projects, national policy has shifted away from funding such critical infrastructure needs as budgetary concerns linger.
The current transportation bill, Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century (MAP-21), offers no new funding for investments in transportation alternatives to relieve congested corridors or encourage smart solutions to these complex problems.
“It’s a sad reality that little has changed since the last report card in 2009,” Corless continued. “Has anything in Washington changed to drastically improve the condition of our roads, bridges and transit systems in the four years since?”
Without new revenue sources, Corless says, the funding problem is only poised to get worse as revenues continue to decline from the federal gas tax, which has not been raised since 1993. Such a lack of necessary revenues may soon leave the federal government unable to perform basic infrastructure maintenance.
Local Implications?
In both 2009 and 2013, the ASCE gave Ohio a C- grade in their infrastructure report card. While the grade places Ohio ahead of the national average, it still translates to 2,462 structurally deficient bridges and approximately 42% of its roadways in “poor” or “mediocre” quality.
While the State of Ohio raised its gas tax in 2006, the extra revenues have not been enough to keep pace with the demand for larger transportation projects like the expansion of I-75 through Cincinnati, the Brent Spence Bridge project, and the long-planned MLK Interchange project, which all currently stand unfunded or only partially funded.
“Some other states aren’t waiting for billions that are unlikely to come and are thinking about ways to make their dollars do more. Like Massachusetts, where the DOT director issued a goal of tripling the number of trips taken by foot, bike and public transportation — reducing the load on roads and bridges that are among the oldest in the country,” explained Stephen Lee Davis, T4A’s Deputy Communications Director.
The City of Cincinnati has been working towards improving some of its worst-rated infrastructure since the last report card was issued in 2009. Since that time, Cincinnati’s Department of Transportation & Engineering (DOTE) has performed a $22 million rehabilitation of the W. Eighth Street Viaduct and is in the midst of a $55 million replacement of the Waldvogel Viaduct which connects the west side with the center city via the Sixth Street Expressway.
Additionally, Cincinnati’s 3,500-foot-long Western Hills Viaduct also is considered structurally deficient. Replacing a span that is nearly twice as long as the longest Ohio River span, and crosses the Midwest’s second busiest rail yard, will be one that is both difficult and costly.
Cincinnati officials say that they are currently studying whether a rehabilitation of the existing 82-year-old, double-decker viaduct or a replacement will be more appropriate.
“That is one of those kind of icons in the Mill Creek Valley that you like to look at,” noted Michael Moore, Cincinnati’s DOTE Director, on The UrbanCincy Podcast. “But we will need to be very cognizant of how we spend the public’s money in making sure we have a good safe mode to get across that area.”
Moore says that the department hopes to wrap up the study on how to fix the Western Hills Viaduct early this spring. Once that is complete, he says that there will be a good idea on how to accomplish that. Where the funding might come for such a large project, however, is still up in the air.