As the new mayor and city council continue to get settled in to their new offices, we would like to suggest a policy reform that should be enacted immediately to help improve the city’s environment, balance its budget and give residents and businesses greater flexibility in terms of their trash collection.
Since the city debuted its new system of trash collection, it has been riddled with complaints from upset citizens and business owners unhappy about not being able to throw away the amount of trash that they generate. This is a problem since reports of illegal dumping have picked up in various neighborhoods.
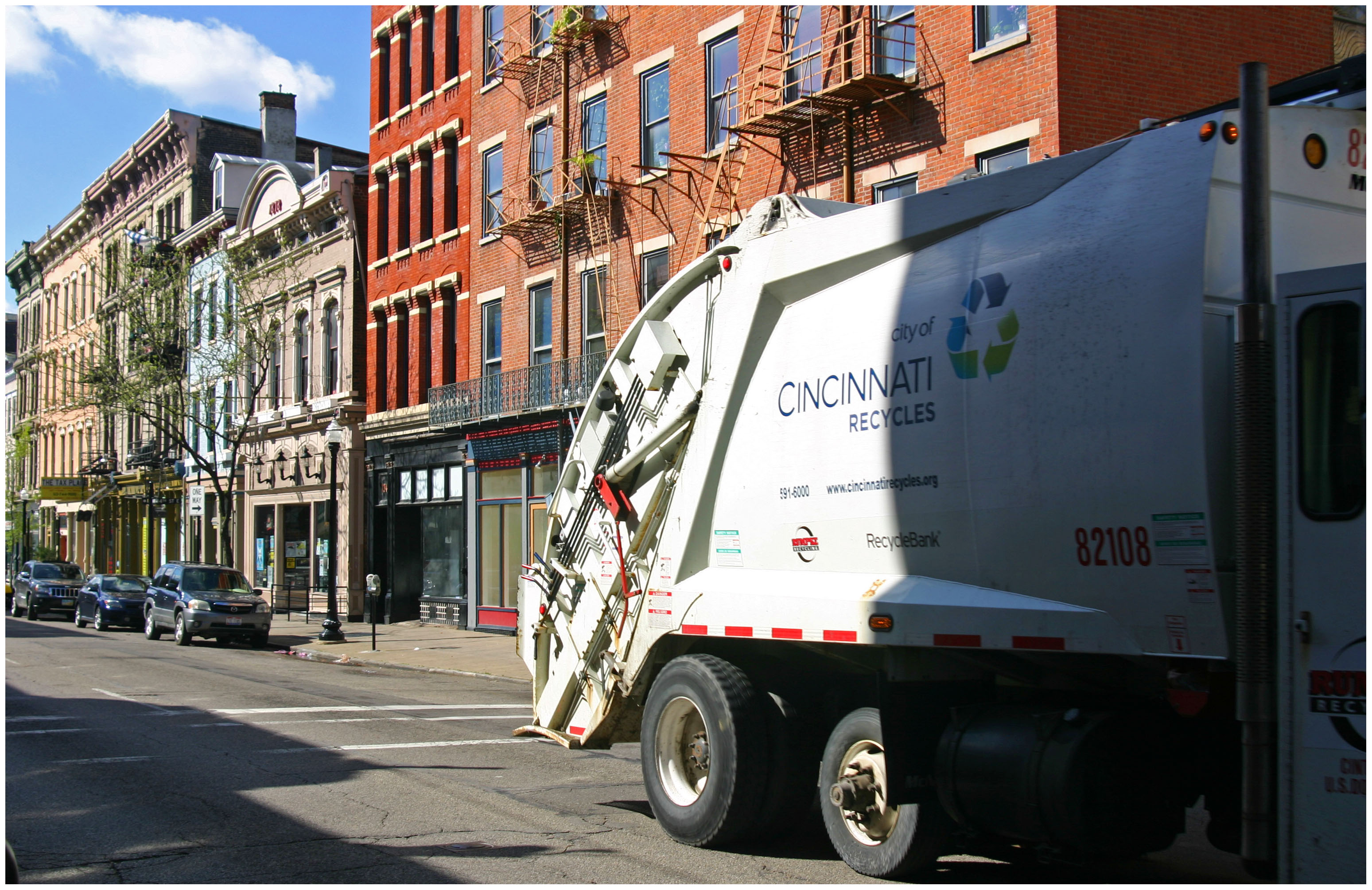
At the same time, the new system represents an improvement over the old in terms of its efficiency. The city is now able to reduce staff levels on each garage truck, avoid safety risks associated with employees lifting and maneuvering heavy trash cans, and boost recycling rates. All of these reforms save the city money and help the city protect its workers from injury on the job.
In order to resolve the ongoing issues, while also preserving the advances that have been made, UrbanCincy urges the new mayor and city council to immediately implement a Pay As You Throw (PAYT) system.
Such a system is supported by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) for its environmental sustainability, economic sustainability and its equity. What the USEPA has noticed is that communities using such a system have realized increased recycling rates, balanced and consistent revenue streams for municipalities looking to offset the costs of their waste collection, and improved equity in terms of how payments are made by the diverse range of users in the system.
As of 2006, USEPA data showed that 243 communities throughout Ohio were utilizing a PAYT system. Cincinnati should be the next.
When implementing a PAYT system, communities are able to choose from charging users a specific fee per bag or can of waste they generate. In communities where the capabilities are available, like Cincinnati, officials can be more precise and charge residents based on the weight of trash they generate.
Due to the potential complexities and higher administrative costs of managing such a variable-rate system, we recommend that city officials set a base rate for each 64-gallon can, with fixed prices for each additional can after that.
This is both a fair and effective means of managing waste collection. It allows users to generate as much or as little trash as they desire without any fear of exceeding the size constraints of their trash can. Those who recycle more, and discard less, are rewarded with lower fees.
If the new mayor and city council would like to pursue a version of this approach that could benefit low-income communities, then we would recommend developing a partnership with a local company or organization, or pursue grant money, that could cover the costs of any user within the city’s established empowerment zones. This would allow the city to continue to improve its financial standing and service delivery, while also working to aid residents and businesses within the neighborhoods that need it most.
In the last full year of budget data, the City of Cincinnati spent $11,320,530 on its Waste Collections Program. This was a $758,740 reduction from the previous year’s expenditures due largely to the elimination of 12 full-time equivalent staff positions. Meanwhile, there is no direct revenue source to pay for this program.
Of course, COAST and its allies successfully pushed through a broadly written Charter amendment in 2011 (Issue 47), which was opposed by the Cincinnati Regional Chamber of Commerce, that prohibits the City from assessing, levying, or collecting taxes or general assessment on real properties, or against the owners or occupants thereof, for the collection of trash, garbage, waste, rubbish or refuse.
What this means is that the City is permanently stuck with an $11-12 million hole in its budget every year. Most communities around the nation and throughout the region already charge their residents and businesses directly for waste collection. Cincinnati has been unique in being able to not directly charge for this service, but times have changed, and so must its policies. Waste collection should collect as much in revenue as is reasonable to help offset the costs to administer the program.
If the new mayor and city council want to get real about passing a structurally balanced budget while not severely degrading the services it provides its residents and businesses, then there should be no question about whether or not to implement a PAYT system as quickly as possible. We cannot afford to let allow an $11.3 million hole sit in our budget.
Implementing a Pay As You Throw system will help structurally balance the city’s budget. It will help improve our environment and the health of our communities. And it will improve the lives for Cincinnati residents and businesses who demand high quality public services with the flexibility they desire in their day-to-day lives. And most importantly, it has the ability to do all of this in an equitable manner for all Cincinnatians.