In late June 2010, 18 individuals from Cincinnati made a trip to Nashville, TN in order to learn more about that city’s form-based code efforts. While on the trip, local officials and community leaders toured three of Nashville’s most notable developments to see first-hand how such land planning initiatives have made a tangible impact there.
In late June 2010, 18 individuals from Cincinnati made a trip to Nashville, TN in order to learn more about that city’s form-based code efforts. While on the trip, local officials and community leaders toured three of Nashville’s most notable developments to see first-hand how such land planning initiatives have made a tangible impact there.
The delegation attending the last of several trips to Nashville included Cincinnati City Councilmembers Laure Quinlivan, Charlie Winburn and Wendell Young; Hamilton Vice Mayor Rob Wile; leaders from Downtown, Walnut Hills, Mt. Auburn, Hyde Park, The Christ Hospital, the Cincinnati Form Based Codes Initiative, and UrbanCincy.
While in Nashville, the delegation visited Lenox Village and The Hill Center. The two new urbanist developments located in Nashville’s suburban communities each have a unique focus as Lenox Village offers a walkable residential neighborhood, while The Hill Center is an upscale commercial district built in a walkable manner.
Inside Lenox Village, the delegation was impressed by the development’s tree-lined streets, wide sidewalks, public gathering spaces, and pocket parks with homes ranging in cost from $84,000 to $350,000. The development also includes a small element of office and retail space, while also providing ten percent of its total housing units as rental.
The area surrounding the upscale, 220,000 square-foot Hill Center development reminded some of the Cincinnati guests of the Kenwood area. But while many of the same upscale retailers were found at both, the physical implementation is much different. According to the developers of The Hill Center, much of the difference comes in the “road diet” that took place to accommodate bicycles, improve sidewalks and pedestrian connections.
“Granbery described the “ping-pong effect” that retailers desire, where a pedestrian can easily cross from one side of the street to the other to reach another retail store that catches his or her eye – even green space should not be so wide as to keep shoppers from crossing the street easily,” described Cincinnati Vice Mayor Roxanne Qualls.
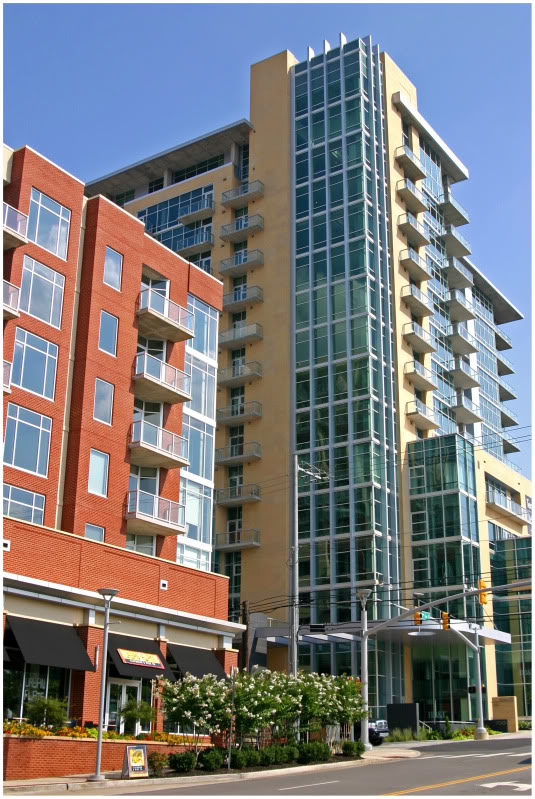
The third development the group toured was The Gulch which is a former railroad center turned mixed-use infill project adjacent to downtown Nashville. Restaurants, live music venues, trendy retail, and condominium towers now occupy the site which has become a popular destination for young people. The Cincinnati delegation also noted that the development project earned a LEED for Neighborhood Development (LEED ND) silver certification for its location, transit access, neighborhood design, green infrastructure and buildings, and its overall design process.
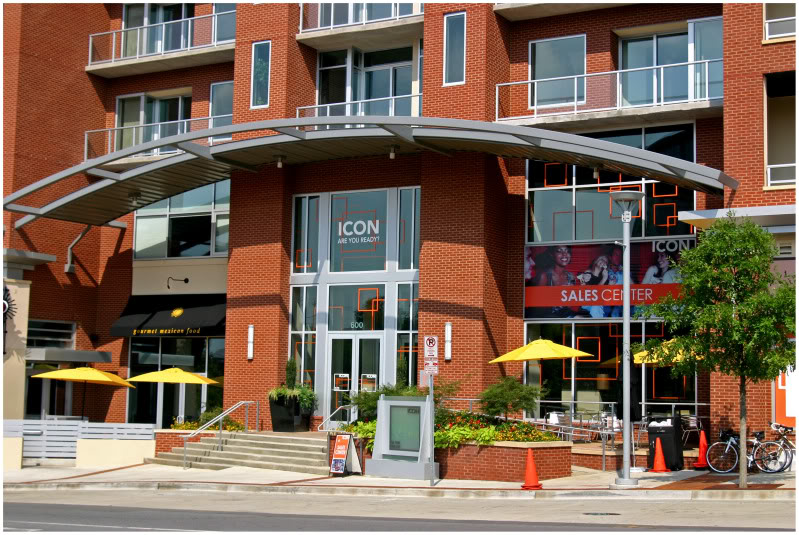



The Gulch is only the ninth neighborhood in America to receive such designation, and the first neighborhood in the south. Since the plan was originally developed in 2002 by MarketStreet Enterprises, the City of Nashville and Davidson County Metropolitan Development & Housing Agency have invested nearly $7 million in infrastructure improvements. The Gulch neighborhood has also required the incorporation of affordable housing in order to receive tax increment financing assistance. Within the ICON, 44 of the total 418 housing units are affordable to those earning 80 percent of median income for the area ($34,000 or less).
The trips to Nashville were taken to help further develop Cincinnati’s initiative to develop form-based codes throughout the city as neighborhoods desire. Should Cincinnati develop such a system of land planning it would become only the third major American city to do so joining Miami and Denver. If all goes according to plan, city officials hope to start implementing the necessary zoning code amendments by fall 2010 with the help of Opticos Design.