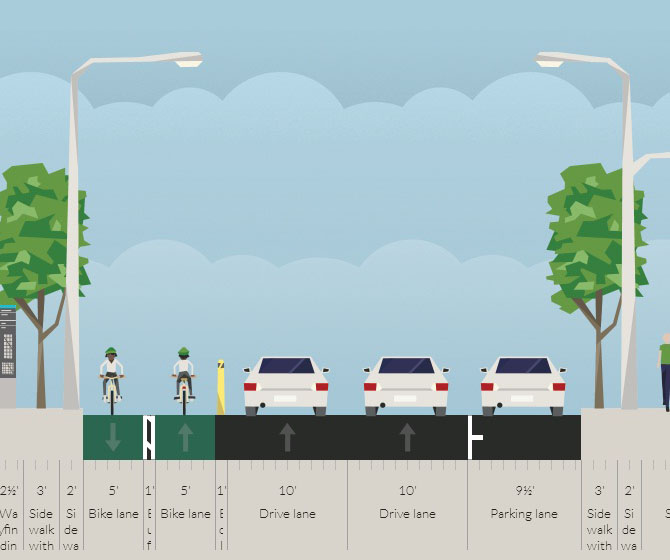
The city will start construction on physically separated bike lanes along Central Parkway, from Downtown to Clifton, this coming spring. Following a community engagement process, a final design was selected in recent weeks, and the large addition to Cincinnati’s bike network is expected to make a significant impact.
Not only will it be one of the most impressive bike facilities installed in the region to-date, but it will also link neighborhoods together that have large percentages of bicyclists. Furthermore, it will link other bike facilities with one another, and come close to linking even more.
Some of the existing facilities include numerous bike lanes and the Mill Creek Greenway, but the Central Parkway bike lanes will come about 12 blocks shy of connecting with the Ohio River Trail, which then links to the Little Miami Scenic Trail.
A two-way cycle track should be built in order to connect the new Central Parkway bike lanes with the Ohio River Trail and beyond.
There are two streets that connect from Central Parkway to the Ohio River Trail along Mehring Way without interruption: Main Street and Elm Street. Both of the streets have one-way traffic heading northbound, but Main Street is considerably more congested with cars and buses heading to Government Square.
Elm Street, however, has some of the least congestion of any north/south street in the Central Business District and could easily connect the Central Parkway cycle track with the Ohio River Trail. A reorganization of the street would need to occur however.
Presently Elm Street, from Central Parkway to Mehring Way, lacks consistency in its design with on-street parking located haphazardly along both sides of the street. A reconfiguration of the street could consolidate all on-street parking to the east side of the street, thus eliminating only a nominal number of on-street parking spaces, and maintain 2 to 3 moving traffic lanes (the parking lane could be restricted during rush hours to allow for a third travel lane).
The Elm Street cycle track, meanwhile, would be located along the west side of the street and be buffered from moving traffic by a row of bollards. Such a redesign of Elm Street would be a bit of a road diet, but one that seems reasonable for this stretch of overbuilt roadway.
Planners with the City’s Department of Transportation & Engineering (DOTE) said that the idea of an Elm Street cycle track had not come up before, and has not been presented to any formal committees or community councils to-date. Such coordination, they say, would need to take place prior to the idea moving forward.
With future phases of The Banks and the yet-to-be-named residential tower on Fourth Street set to begin construction soon, there seems to be an opportunity to rebuild this roadway along with those projects. This would help offset some of the costs and make for a more seamless transition.
Projects like this are low-hanging fruit for the new mayor and council, should they wish to pursue investments that improve the city’s bike infrastructure. They should work with the bike community and come up with a strategy that provides a clear path forward to make this happen.
An Elm Street cycle track like this would provide a critical link in the region’s bike network, make the street safer, more accommodating to more users and more attractive to those who currently find themselves along the now bleak and desolate stretch of roadway. Let’s get to work.