When thinking of the mega-cities in Asia, one does not often first think of sustainability or environmental stewardship. But the reality, as I experienced in Seoul, is much different from the perception.
As the 24.5 million-person mega-city continues to grow both up and out, Korean leaders have turned a watchful eye to environmental sustainability. Projects like the removal of an elevated highway to restore a stream through the heart of the city, riverfront park development, investments in transit, and a massive transition to electric-powered buses are powering the world’s third largest city towards a sustainable future that was once considered inconceivable.
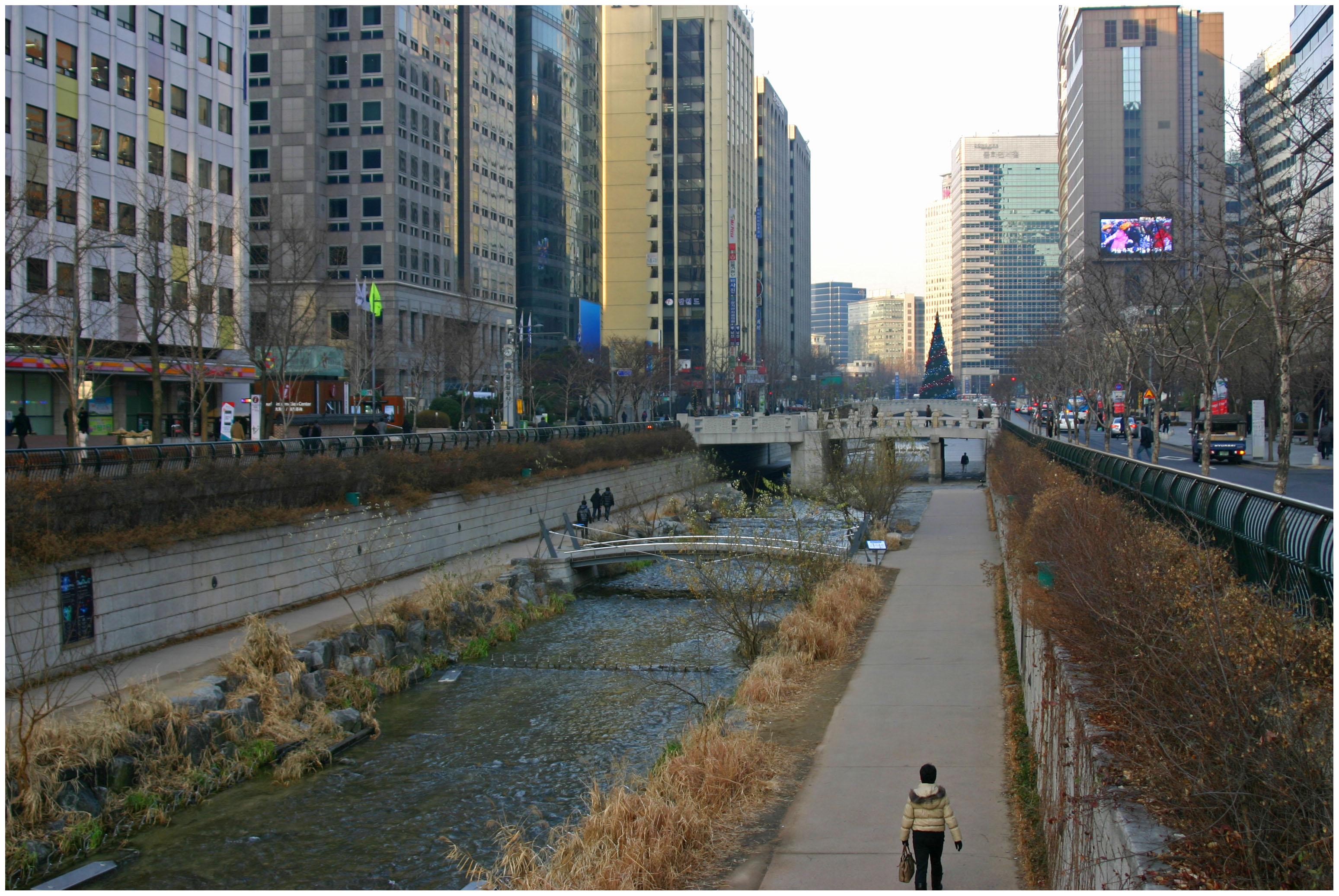
Cheonggyecheon Stream Restoration:
In the heart of Seoul’s Jongno-gu is a sub-level stream. The Cheonggyecheon Stream stretches six kilometers and follows the path of what was previously an offensive elevated highway. The highway was removed and replaced by the stream and two narrow parallel roadways.
While the $900 million project received much criticism and pushback when it began in 2003, the result has been one of the most successful projects of Lee Myung-Bak’s administration. Since the stream opened in 2005, Koreans, and visitors alike, flock to the stream for casual strolls, use it as a place to jog or relax, and the stream has become the epicenter for major cultural events like the annual Seoul Lantern Festival.
Environmentally speaking, the restoration of the Cheonggyecheon Stream has helped to increase wildlife in the area, cool down the urban heat island effect in the immediate vicinity by an average of 38.5 degrees, decrease automobile traffic, and increase transit ridership.
What the stream does so successfully is provide a corridor of open space in an otherwise extremely busy and crowded city center. It serves as both a welcoming getaway as much as a symbol for the future of a more eco-friendly Seoul.
Banpo Hangang Park:
If you head south from the Cheonggyecheon you will pass by Namsan Tower and park, U.S. Army Garrison Yongsan, the famed Itaewon neighborhood along with several other neighborhoods. At that point you will reach the Han River. There the southern bank of the river has, in recent years, been transformed into a world-class park in an effort to restore the river’s edge while also creating a dynamic new park space for those living in the otherwise congested Seoul.
The project began in 2007 and saw its first elements come online in April 2009. Inside the linear park visitors are able to find playgrounds, an inline skating track, soccer field, basketball courts, bike lanes and a rental shop, picnic locations and other recreational opportunities.
The park is part of the larger Hangang Renaissance Project, but represents a movement taking place around the world to transform flood-prone areas into functional park spaces. In Seoul, the addition of open space is of even greater importance than many other cities, but the Banpo Hangang Park is similar to the string of riverfront parks in Cincinnati including the new Central Riverfront Park, Sawyer Point, Bicentennial Commons, and the International Friendship Park.
Transit & Electric Buses:
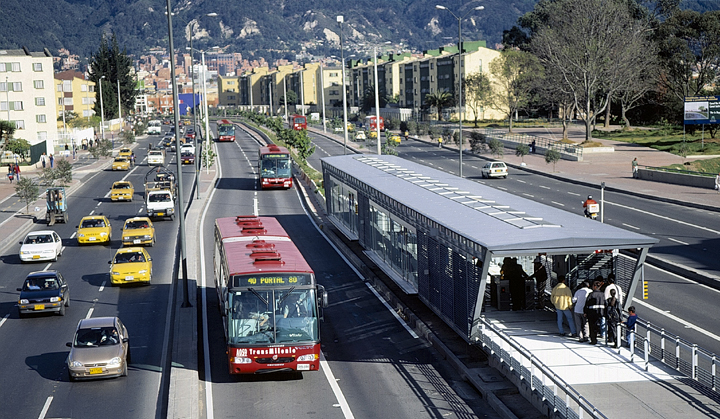
In addition to having the world’s third largest subway system and a truly robust bus network, Seoul officials have announced that they intend to convert the city’s massive bus fleet to electric. In fact, transportation officials have announced that half (120,000 buses) of its entire fleet will be electric by 2020 – by far the most aggressive goal anywhere in the world.
The conversion of Seoul’s buses to electric is matched by their willingness to invest in their system. The city boasts a large bus rapid transit system that was smartly copied from Germany, fast and timely service, commuter and circulator lines, and a pay card system that integrates with taxis and trains all throughout the Republic of Korea.
Combine these projects with the wave of green building developments and other cultural movements towards sustainability and you have yourself a surprising mega-city in east Asia that has shifted its attention from simply growing as fast as possible, to growing the best way possible.