Last fall UrbanCincy partnered with the Niehoff Urban Studio on an event that highlighted the work of an interdisciplinary group of students. That semester engineering and planning students focused on urban mobility and looked at bikeways and bus rapid transit ideas within the city.
Last fall UrbanCincy partnered with the Niehoff Urban Studio on an event that highlighted the work of an interdisciplinary group of students. That semester engineering and planning students focused on urban mobility and looked at bikeways and bus rapid transit ideas within the city.
Each of the student groups presented their final research and findings to fellow academics and industry experts from around the region. We then gathered a group of transit and bike experts to engage in a panel discussion about the student’s proposals and about transportation in the region in general.
Throughout the course of the day, we asked members of the public who attended to vote on their favorite proposal. The winner was a bus rapid transit corridor along Hamilton Avenue that focused heavily on a transit-oriented development (TOD) in Northside where The Gantry is now being built.
The six-person team consisted of Tyler Kiefer, Benjamin Lafferty, Christopher Murphy, Michael Orth and Michael Walsh from the College of Engineering & Applied Science and Alexander Cassini from the College of Design, Architecture, Art & Planning.
First and foremost, the group said that their Hamilton BRT Line would most closely resemble Cleveland’s highly publicized HealthLine, which is the highest-rated BRT line, by far, in North America. The group also examined lines in Pittsburgh and Kansas City.
One of the main reasons for the comparisons to Cleveland is the similarities between the corridors. In both Cincinnati and Cleveland, the corridors connect neighborhoods under-served by transit to institutional services, while also providing greater mobility.
“The 2010 U.S. Census has shown how the population along Hamilton Avenue has less access to quick and reliable means of transportation when compared to the stats of Cincinnati and Ohio as a whole,” explained Masters of Community Planning student Alexander Cassini. “This lack of mobility directly affects citizens’ access to essential services and employment opportunities.”
Their research found that Metro’s #17 bus route, which most closely aligns with their proposed BRT corridor, currently averages weekday ridership of about 4,500 people. Furthermore, they found that approximately 17% of the households along the corridor have no car, 10% of the commuters identify as bus riders and there are 6,387 people living per square mile.
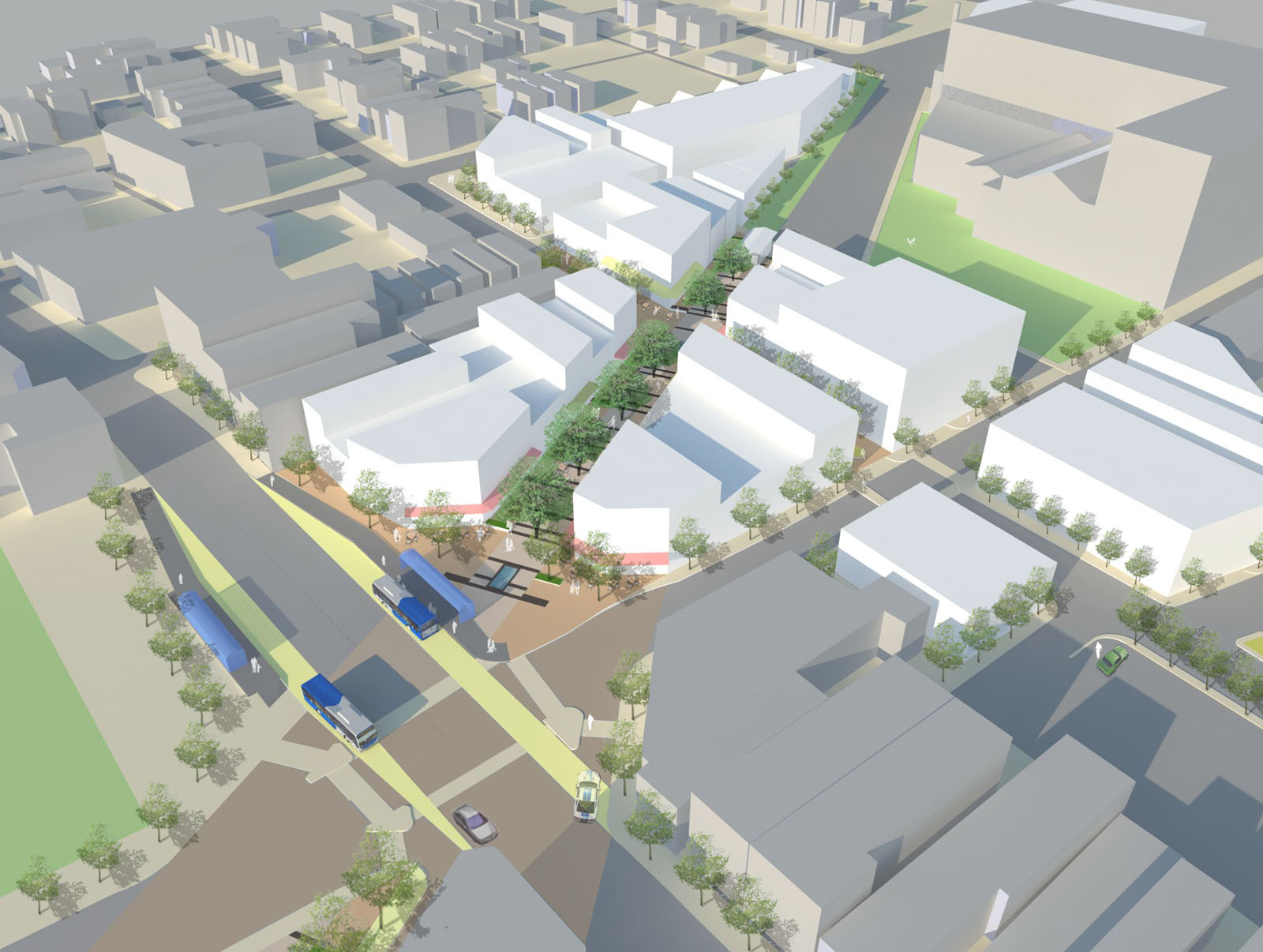
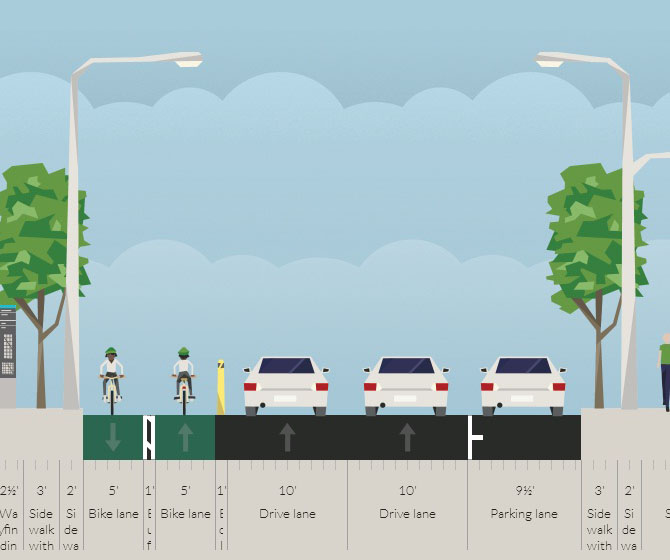
The proposed BRT corridor runs from Downtown to North College Hill, and the engineering and planning students saw this particular corridor as a major opportunity to spread investment and attention from the center city to additional neighborhoods that would take advantage of the BRT route’s 12 stations spaced out between one-half mile to three-fourths of a mile apart that would ensure faster and more efficient service. Each of the 12 station locations, Cassini notes, was selected due to its significant population and employment nearby.
“Northside and North College Hill are historic places in the city and present a great opportunity for Cincinnati to keep growing as a city,” noted civil engineering student Michael Orth.
Orth went on to say that while one of the positives of this corridor was the amount of people and businesses it could positively impact, the area’s congestion was also one of the team’s greatest challenges, stating, “There is very little room to implement a bus only lane throughout the corridor, which would be ideal for a BRT line.”
To help address this situation the group said that they envision a bus only lane, or a hybrid lane for buses and cars depending on the hour, through the congested portions of the route. Although not recommended, if a hybrid lane was determined to not be satisfactory Orth said that further study could be done to examine whether there would be enough benefit to remove on-street parking in order to provide for a consistent, dedicated bus only lane.
Other technology to help facilitate the quick movement of buses along the corridor would include arrival detection at traffic signals so that the lights can change in order to accommodate an approaching bus.
Existing Metro bus service, they said, would largely be redeployed to avoid redundancy, but some would remain since local buses stop more frequently – potentially creating a corridor of localized bus and express BRT service.
Hamilton Avenue BRT in Metro*Plus Context
One area where the Southwest Ohio Regional Transit Authority (SORTA) has already begun enhancing bus service is along Montgomery Road, which connects Downtown with the Kenwood area. That new Metro*Plus service, while not full BRT, is a step in the right direction according to the University of Cincinnati students, and has already seen ridership triple since its upgrade.
“Metro*Plus service is good but it is only the first step towards a true BRT system for the Cincinnati metropolitan area,” Cassini cautioned. “Metro*Plus service can be even more efficient, and effective if totally dedicated lanes and other additional features are added.”
Reading Road, where Metro began operating articulated buses in 2010, is actually the region’s most heavily utilized bus corridor with Hamilton Avenue coming in second and Montgomery Road third. If Metro is to continue to build out its enhanced bus service, or full-on BRT operations, then Hamilton Avenue may very well be the next logical choice.
What helped the group’s proposal stand out from other presentations was its focus on the TOD in Northside. With a $13 million mixed-use project coming out of the ground on that site now, the group reflected on their own proposal.
While the team had collectively noted the large, clean open space as being one of the huge benefits of the site, it also made it particularly valuable in their opinion. As a result, several of the group members, while encouraged about the private investment, were also a bit underwhelmed by the Indianapolis-based Milhaus Developers’ architectural design.
Both Cassini and Orth mentioned that they would be interested in working full-time in the transportation industry someday, but for different reasons. When asked to briefly compare the wide variety of transportation projects current in the planning or development stages around the region, there was a uniform response that their excitement is for the Cincinnati Streetcar.
“Although the planned streetcar line does not expand sufficiently in our eyes, we believe it would be an incredible economic development booster for Cincinnati’s downtown and overall urban core,” Cassini explained. “The overall transportation efforts around Cincinnati will eventually pay off to form a comprehensive and more easily navigable system than today.”
The Niehoff Urban Studio is currently working with a new set of students on designs for the Wasson Corridor, which runs through several of Cincinnati’s eastern neighborhoods. This is another topic that was examined by one of the interdisciplinary groups of planners and engineers last year. UrbanCincy is once again partnering with the Niehoff Urban Studio and will be organizing a similar showcase and panel discussion in 2014.